Page 172 - Aeronautical Engineer Data Book
P. 172
Aircraft performance 143
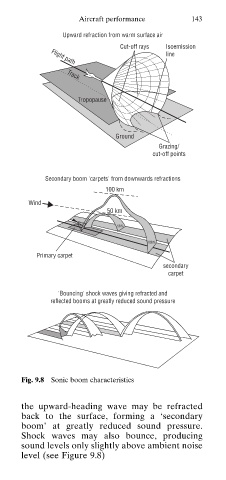
Upward refraction from warm surface air
Cut-off rays Isoemission
line
Flight path
Track
Tropopause
Ground
Grazing/
cut-off points
Secondary boom 'carpets' from downwards refractions
100 km
Wind
50 km
50%
100%
Primary carpet
secondary
carpet
'Bouncing' shock waves giving refracted and
reflected booms at greatly reduced sound pressure
Fig. 9.8 Sonic boom characteristics
the upward-heading wave may be refracted
back to the surface, forming a ‘secondary
boom’ at greatly reduced sound pressure.
Shock waves may also bounce, producing
sound levels only slightly above ambient noise
level (see Figure 9.8)