Page 244 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 244
05_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 3:46 pm Page 223
Wet and Dry Scrubbing 223
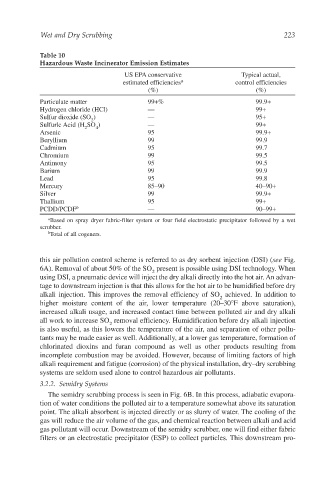
Table 10
Hazardous Waste Incinerator Emission Estimates
US EPA conservative Typical actual,
estimated efficiencies a control efficiencies
(%) (%)
Particulate matter 99+% 99.9+
Hydrogen chloride (HCl) — 99+
Sulfur dioxide (SO ) — 95+
2
Sulfurlc Acid (H SO ) — 99+
2 4
Arsenic 95 99.9+
Beryllium 99 99.9
Cadmium 95 99.7
Chromium 99 99.5
Antimony 95 99.5
Barium 99 99.9
Lead 95 99.8
Mercury 85–90 40–90+
Silver 99 99.9+
Thallium 95 99+
PCDD/PCDF b — 90–99+
a Based on spray dryer fabric-filter system or four field electrostatic precipitator followed by a wet
scrubber.
b Total of all cogeners.
this air pollution control scheme is referred to as dry sorbent injection (DSI) (see Fig.
6A). Removal of about 50% of the SO present is possible using DSI technology. When
2
using DSI, a pneumatic device will inject the dry alkali directly into the hot air. An advan-
tage to downstream injection is that this allows for the hot air to be humidified before dry
alkali injection. This improves the removal efficiency of SO achieved. In addition to
2
higher moisture content of the air, lower temperature (20–30°F above saturation),
increased alkali usage, and increased contact time between polluted air and dry alkali
all work to increase SO removal efficiency. Humidification before dry alkali injection
2
is also useful, as this lowers the temperature of the air, and separation of other pollu-
tants may be made easier as well. Additionally, at a lower gas temperature, formation of
chlorinated dioxins and furan compound as well as other products resulting from
incomplete combustion may be avoided. However, because of limiting factors of high
alkali requirement and fatigue (corrosion) of the physical installation, dry–dry scrubbing
systems are seldom used alone to control hazardous air pollutants.
3.2.2. Semidry Systems
The semidry scrubbing process is seen in Fig. 6B. In this process, adiabatic evapora-
tion of water conditions the polluted air to a temperature somewhat above its saturation
point. The alkali absorbent is injected directly or as slurry of water. The cooling of the
gas will reduce the air volume of the gas, and chemical reaction between alkali and acid
gas pollutant will occur. Downstream of the semidry scrubber, one will find either fabric
filters or an electrostatic precipitator (ESP) to collect particles. This downstream pro-