Page 27 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 27
01_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 11:45 am Page 8
8 Lawrence K. Wang et al.
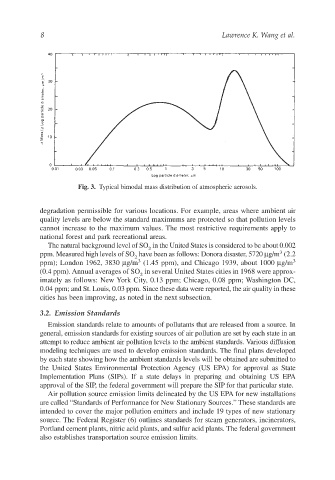
Fig. 3. Typical bimodal mass distribution of atmospheric aerosols.
degradation permissible for various locations. For example, areas where ambient air
quality levels are below the standard maximums are protected so that pollution levels
cannot increase to the maximum values. The most restrictive requirements apply to
national forest and park recreational areas.
The natural background level of SO in the United States is considered to be about 0.002
2
3
ppm. Measured high levels of SO have been as follows: Donora disaster, 5720 µg/m (2.2
2
3
ppm); London 1962, 3830 µg/m (1.45 ppm), and Chicago 1939, about 1000 µg/m 3
(0.4 ppm). Annual averages of SO in several United States cities in 1968 were approx-
2
imately as follows: New York City, 0.13 ppm; Chicago, 0.08 ppm; Washington DC,
0.04 ppm; and St. Louis, 0.03 ppm. Since these data were reported, the air quality in these
cities has been improving, as noted in the next subsection.
3.2. Emission Standards
Emission standards relate to amounts of pollutants that are released from a source. In
general, emission standards for existing sources of air pollution are set by each state in an
attempt to reduce ambient air pollution levels to the ambient standards. Various diffusion
modeling techniques are used to develop emission standards. The final plans developed
by each state showing how the ambient standards levels will be obtained are submitted to
the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) for approval as State
Implementation Plans (SIPs). If a state delays in preparing and obtaining US EPA
approval of the SIP, the federal government will prepare the SIP for that particular state.
Air pollution source emission limits delineated by the US EPA for new installations
are called “Standards of Performance for New Stationary Sources.” These standards are
intended to cover the major pollution emitters and include 19 types of new stationary
source. The Federal Register (6) outlines standards for steam generators, incinerators,
Portland cement plants, nitric acid plants, and sulfur acid plants. The federal government
also establishes transportation source emission limits.