Page 282 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 282
05_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 3:51 pm Page 261
Wet and Dry Scrubbing 261
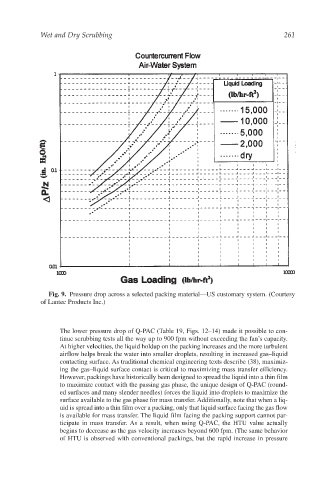
Fig. 9. Pressure drop across a selected packing material—US customary system. (Courtesy
of Lantec Products Inc.)
The lower pressure drop of Q-PAC (Table 19, Figs. 12–14) made it possible to con-
tinue scrubbing tests all the way up to 900 fpm without exceeding the fan’s capacity.
At higher velocities, the liquid holdup on the packing increases and the more turbulent
airflow helps break the water into smaller droplets, resulting in increased gas–liquid
contacting surface. As traditional chemical engineering texts describe (38), maximiz-
ing the gas–liquid surface contact is critical to maximizing mass transfer efficiency.
However, packings have historically been designed to spread the liquid into a thin film
to maximize contact with the passing gas phase, the unique design of Q-PAC (round-
ed surfaces and many slender needles) forces the liquid into droplets to maximize the
surface available to the gas phase for mass transfer. Additionally, note that when a liq-
uid is spread into a thin film over a packing, only that liquid surface facing the gas flow
is available for mass transfer. The liquid film facing the packing support cannot par-
ticipate in mass transfer. As a result, when using Q-PAC, the HTU value actually
begins to decrease as the gas velocity increases beyond 600 fpm. (The same behavior
of HTU is observed with conventional packings, but the rapid increase in pressure