Page 381 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 381
08_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 4:26 pm Page 357
Thermal Oxidation 357
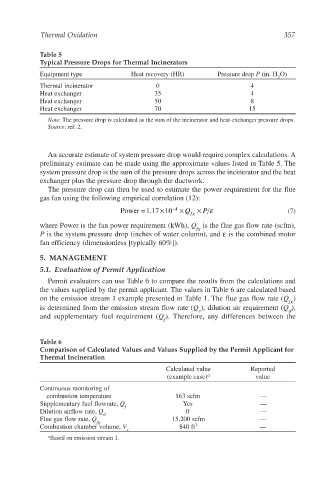
Table 5
Typical Pressure Drops for Thermal Incinerators
Equipment type Heat recovery (HR) Pressure drop P (in. H O)
2
Thermal incinerator 0 4
Heat exchanger 35 4
Heat exchanger 50 8
Heat exchanger 70 15
Note: The pressure drop is calculated as the sum of the incinerator and heat-exchanger pressure drops.
Source: ref. 2.
An accurate estimate of system pressure drop would require complex calculations. A
preliminary estimate can be made using the approximate values listed in Table 5. The
system pressure drop is the sum of the pressure drops across the incinerator and the heat
exchanger plus the pressure drop through the ductwork.
The pressure drop can then be used to estimate the power requirement for the flue
gas fan using the following empirical correlation (12):
×
Power =1.17 10 –4 × Q fg × P ε (7)
where Power is the fan power requirement (kWh), Q is the flue gas flow rate (scfm),
fg
P is the system pressure drop (inches of water column), and ε is the combined motor
fan efficiency (dimensionless [typically 60%]).
5. MANAGEMENT
5.1. Evaluation of Permit Application
Permit evaluators can use Table 6 to compare the results from the calculations and
the values supplied by the permit applicant. The values in Table 6 are calculated based
on the emission stream 1 example presented in Table 1. The flue gas flow rate (Q )
fg
is determined from the emission stream flow rate (Q ), dilution air requirement (Q ),
e d
and supplementary fuel requirement (Q ). Therefore, any differences between the
f
Table 6
Comparison of Calculated Values and Values Supplied by the Permit Applicant for
Thermal Incineration
Calculated value Reported
(example case) a value
Continuous monitoring of
combustion temperature 163 scfm —
Supplementary fuel flowrate, Q Yes —
f
Dilution airflow rate, Q 0 —
d
Flue gas flow rate, Q 15,200 scfm —
fg
Combustion chamber volume, V 840 ft 3 —
c
a Based on emission stream 1.