Page 376 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 376
08_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 4:26 pm Page 352
352 Lawrence K. Wang et al.
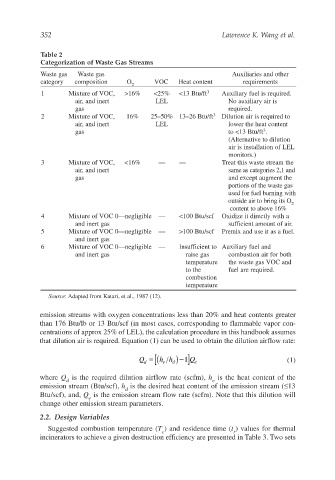
Table 2
Categorization of Waste Gas Streams
Waste gas Waste gas Auxiliaries and other
category composition O VOC Heat content requirements
2
1 Mixture of VOC, >16% <25% <13 Btu/ft 3 Auxiliary fuel is required.
air, and inert LEL No auxiliary air is
gas required.
2 Mixture of VOC, 16% 25–50% 13–26 Btu/ft 3 Dilution air is required to
air, and inert LEL lower the heat content
3
gas to <13 Btu/ft .
(Alternative to dilution
air is installation of LEL
monitors.)
3 Mixture of VOC, <16% — — Treat this waste stream the
air, and inert same as categories 2,1 and
gas and except augment the
portions of the waste gas
used for fuel burning with
outside air to bring its O
2
content to above 16%
4 Mixture of VOC 0—negligible — <100 Btu/scf Oxidize it directly with a
and inert gas sufficient amount of air.
5 Mixture of VOC 0—negligible — >100 Btu/scf Premix and use it as a fuel.
and inert gas
6 Mixture of VOC 0—negligible — Insufficient to Auxiliary fuel and
and inert gas raise gas combustion air for both
temperature the waste gas VOC and
to the fuel are required.
combustion
temperature
Source: Adapted from Katari, et al., 1987 (12).
emission streams with oxygen concentrations less than 20% and heat contents greater
than 176 Btu/lb or 13 Btu/scf (in most cases, corresponding to flammable vapor con-
centrations of approx 25% of LEL), the calculation procedure in this handbook assumes
that dilution air is required. Equation (1) can be used to obtain the dilution airflow rate:
Q = ( [ e ]
d h h ) −1 Q (1)
e
d
where Q is the required dilution airflow rate (scfm), h is the heat content of the
d e
emission stream (Btu/scf), h is the desired heat content of the emission stream (≤13
d
Btu/scf), and, Q is the emission stream flow rate (scfm). Note that this dilution will
e
change other emission stream parameters.
2.2. Design Variables
Suggested combustion temperature (T ) and residence time (t ) values for thermal
c r
incinerators to achieve a given destruction efficiency are presented in Table 3. Two sets