Page 438 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 438
10_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 5:10 pm Page 410
410 Lawrence K.Wang et al.
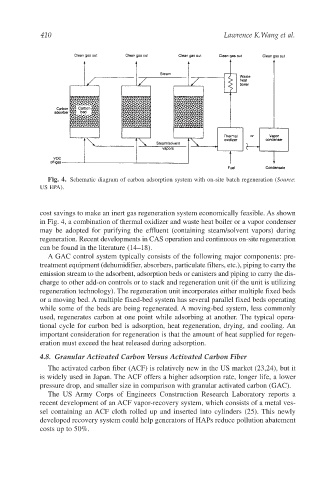
Fig. 4. Schematic diagram of carbon adsorption system with on-site batch regeneration (Source:
US EPA).
cost savings to make an inert gas regeneration system economically feasible. As shown
in Fig. 4, a combination of thermal oxidizer and waste heat boiler or a vapor condenser
may be adopted for purifying the effluent (containing steam/solvent vapors) during
regeneration. Recent developments in CAS operation and continuous on-site regeneration
can be found in the literature (14–18).
A GAC control system typically consists of the following major components: pre-
treatment equipment (dehumidifier, absorbers, particulate filters, etc.), piping to carry the
emission stream to the adsorbent, adsorption beds or canisters and piping to carry the dis-
charge to other add-on controls or to stack and regeneration unit (if the unit is utilizing
regeneration technology). The regeneration unit incorporates either multiple fixed beds
or a moving bed. A multiple fixed-bed system has several parallel fixed beds operating
while some of the beds are being regenerated. A moving-bed system, less commonly
used, regenerates carbon at one point while adsorbing at another. The typical opera-
tional cycle for carbon bed is adsorption, heat regeneration, drying, and cooling. An
important consideration for regeneration is that the amount of heat supplied for regen-
eration must exceed the heat released during adsorption.
4.8. Granular Activated Carbon Versus Activated Carbon Fiber
The activated carbon fiber (ACF) is relatively new in the US market (23,24), but it
is widely used in Japan. The ACF offers a higher adsorption rate, longer life, a lower
pressure drop, and smaller size in comparison with granular activated carbon (GAC).
The US Army Corps of Engineers Construction Research Laboratory reports a
recent development of an ACF vapor-recovery system, which consists of a metal ves-
sel containing an ACF cloth rolled up and inserted into cylinders (25). This newly
developed recovery system could help generators of HAPs reduce pollution abatement
costs up to 50%.