Page 87 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 87
02_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 12:40 pm Page 67
Fabric Filtration 67
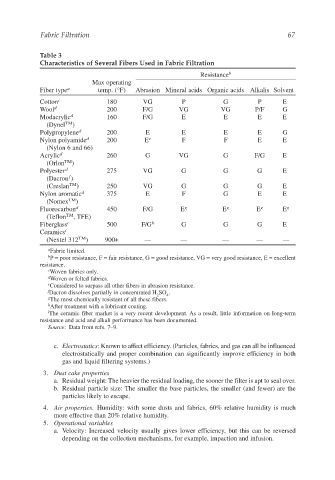
Table 3
Characteristics of Several Fibers Used in Fabric Filtration
Resistance b
Max operating
Fiber type a temp. (°F) Abrasion Mineral acids Organic acids Alkalis Solvent
Cotton c 180 VG P G P E
Wool d 200 F/G VG VG P/F G
Modacrylic d 160 F/G E E E E
(Dynel TM )
Polypropylene d 200 E E E E G
Nylon polyamide d 200 E e F F E E
(Nylon 6 and 66)
Acrylic d 260 G VG G F/G E
(Orlon TM )
Polyester d 275 VG G G G E
f
(Dacron )
(Creslan TM ) 250 VG G G G E
Nylon aromatic d 375 E F G E E
(Nomex TM )
Fluorocarbon d 450 F/G E g E g E g E g
(Teflon TM , TFE)
Fiberglass c 500 F/G h G G G E
Ceramics i
(Nextel 312 TM ) 900+ — — — — —
a Fabric limited.
b P = poor resistance, F = fair resistance, G = good resistance, VG = very good resistance, E = excellent
resistance.
c Woven fabrics only.
d Woven or felted fabrics.
e Considered to surpass all other fibers in abrasion resistance.
f Dacron dissolves partially in concentrated H SO .
2
g The most chemically resistant of all these fibers. 4
h After treatment with a lubricant coating.
i The ceramic fiber market is a very recent development. As a result, little information on long-term
resistance and acid and alkali performance has been documented.
Source: Data from refs. 7–9.
c. Electrostatics: Known to affect efficiency. (Particles, fabrics, and gas can all be influenced
electrostatically and proper combination can significantly improve efficiency in both
gas and liquid filtering systems.)
3. Dust cake properties
a. Residual weight: The heavier the residual loading, the sooner the filter is apt to seal over.
b. Residual particle size: The smaller the base particles, the smaller (and fewer) are the
particles likely to escape.
4. Air properties. Humidity: with some dusts and fabrics, 60% relative humidity is much
more effective than 20% relative humidity.
5. Operational variables
a. Velocity: Increased velocity usually gives lower efficiency, but this can be reversed
depending on the collection mechanisms, for example, impaction and infusion.