Page 398 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 398
12.6 CO 2 Separation by Absorption 377
18
16
363 K
14
Pressure (MPa) 10 8 333 K
12
6
273 K
4
2
0
0 1 2 3 4 5
Molality (mole/kg)
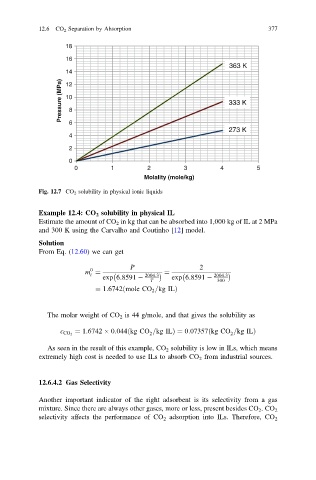
Fig. 12.7 CO 2 solubility in physical ionic liquids
Example 12.4: CO 2 solubility in physical IL
Estimate the amount of CO 2 in kg that can be absorbed into 1,000 kg of IL at 2 MPa
and 300 K using the Carvalho and Coutinho [12] model.
Solution
From Eq. (12.60) we can get
P 2
0
m ¼ 2004:3 ¼ 2004:3
i
exp 6:8591 exp 6:8591
T 300
¼ 1:6742 mole CO 2 =kg ILð Þ
The molar weight of CO 2 is 44 g/mole, and that gives the solubility as
ð
ð
¼ 1:6742 0:044 kg CO =kg ILÞ ¼ 0:07357 kg CO =kg ILÞ
c CO 2 2 2
As seen in the result of this example, CO 2 solubility is low in ILs, which means
extremely high cost is needed to use ILs to absorb CO 2 from industrial sources.
12.6.4.2 Gas Selectivity
Another important indicator of the right adsorbent is its selectivity from a gas
mixture. Since there are always other gases, more or less, present besides CO 2 .CO 2
selectivity affects the performance of CO 2 adsorption into ILs. Therefore, CO 2