Page 40 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 40
1.4 Roots of Air Pollution and GHGs 13
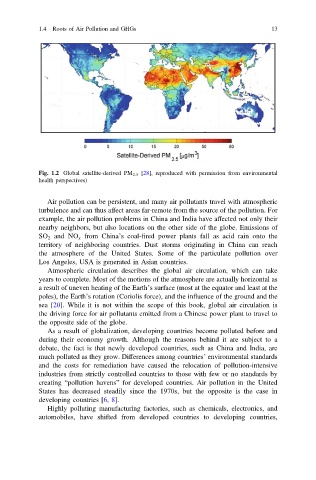
Fig. 1.2 Global satellite-derived PM 2.5 [28], reproduced with permission from environmental
health perspectives)
Air pollution can be persistent, and many air pollutants travel with atmospheric
turbulence and can thus affect areas far-remote from the source of the pollution. For
example, the air pollution problems in China and India have affected not only their
nearby neighbors, but also locations on the other side of the globe. Emissions of
SO 2 and NO x from China’s coal-fired power plants fall as acid rain onto the
territory of neighboring countries. Dust storms originating in China can reach
the atmosphere of the United States. Some of the particulate pollution over
Los Angeles, USA is generated in Asian countries.
Atmospheric circulation describes the global air circulation, which can take
years to complete. Most of the motions of the atmosphere are actually horizontal as
a result of uneven heating of the Earth’s surface (most at the equator and least at the
poles), the Earth’s rotation (Coriolis force), and the influence of the ground and the
sea [20]. While it is not within the scope of this book, global air circulation is
the driving force for air pollutants emitted from a Chinese power plant to travel to
the opposite side of the globe.
As a result of globalization, developing countries become polluted before and
during their economy growth. Although the reasons behind it are subject to a
debate, the fact is that newly developed countries, such as China and India, are
much polluted as they grow. Differences among countries’ environmental standards
and the costs for remediation have caused the relocation of pollution-intensive
industries from strictly controlled countries to those with few or no standards by
creating “pollution havens” for developed countries. Air pollution in the United
States has decreased steadily since the 1970s, but the opposite is the case in
developing countries [6, 8].
Highly polluting manufacturing factories, such as chemicals, electronics, and
automobiles, have shifted from developed countries to developing countries,