Page 438 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 438
418 13 Nanoaerosol
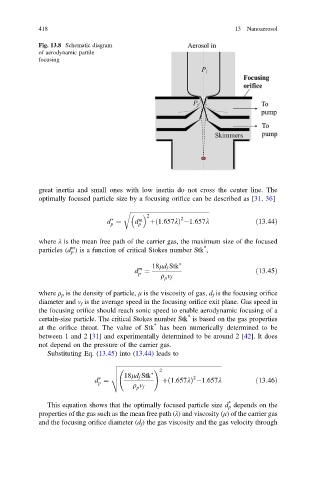
Fig. 13.8 Schematic diagram
of aerodynamic partile
focusing
great inertia and small ones with low inertia do not cross the center line. The
optimally focused particle size by a focusing orifice can be described as [31, 36]
r ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi
2
m 2
d ¼ d þ 1:657kÞ 1:657k ð13:44Þ
ð
p p
where λ is the mean free path of the carrier gas, the maximum size of the focused
m
*
particles (d p ) is a function of critical Stokes number Stk ,
18ld f Stk
m
d ¼ ð13:45Þ
p
p
q v f
where ρ p is the density of particle, μ is the viscosity of gas, d f is the focusing orifice
diameter and v f is the average speed in the focusing orifice exit plane. Gas speed in
the focusing orifice should reach sonic speed to enable aerodynamic focusing of a
*
certain-size particle. The critical Stokes number Stk is based on the gas properties
*
at the orifice throat. The value of Stk has been numerically determined to be
between 1 and 2 [31] and experimentally determined to be around 2 [42]. It does
not depend on the pressure of the carrier gas.
Substituting Eq. (13.45) into (13.44) leads to
v ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi
2
!
u
18ld f Stk 2
u
t
d ¼ þ 1:657kÞ 1:657k ð13:46Þ
ð
p
q v f
p
*
This equation shows that the optimally focused particle size d p depends on the
properties of the gas such as the mean free path (λ) and viscosity (μ) of the carrier gas
and the focusing orifice diameter (d f ) the gas viscosity and the gas velocity through