Page 126 - Air and Gas Drilling Manual
P. 126
4-12 Air and Gas Drilling Manual
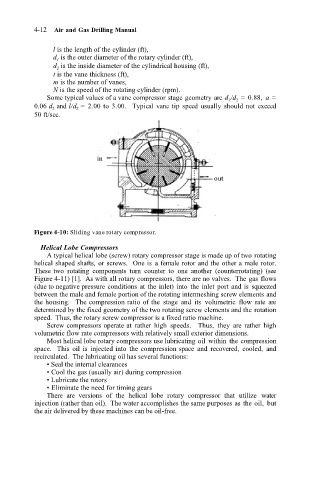
l is the length of the cylinder (ft),
d 1 is the outer diameter of the rotary cylinder (ft),
d 2 is the inside diameter of the cylindrical housing (ft),
t is the vane thickness (ft),
m is the number of vanes,
N is the speed of the rotating cylinder (rpm).
Some typical values of a vane compressor stage geometry are d 1 /d 2 = 0.88, a =
0.06 d 2 and l/d 2 = 2.00 to 3.00. Typical vane tip speed usually should not exceed
50 ft/sec.
in
out
Figure 4-10: Sliding vane rotary compressor.
Helical Lobe Compressors
A typical helical lobe (screw) rotary compressor stage is made up of two rotating
helical shaped shafts, or screws. One is a female rotor and the other a male rotor.
These two rotating components turn counter to one another (counterrotating) (see
Figure 4-11) [1]. As with all rotary compressors, there are no valves. The gas flows
(due to negative pressure conditions at the inlet) into the inlet port and is squeezed
between the male and female portion of the rotating intermeshing screw elements and
the housing. The compression ratio of the stage and its volumetric flow rate are
determined by the fixed geometry of the two rotating screw elements and the rotation
speed. Thus, the rotary screw compressor is a fixed ratio machine.
Screw compressors operate at rather high speeds. Thus, they are rather high
volumetric flow rate compressors with relatively small exterior dimensions.
Most helical lobe rotary compressors use lubricating oil within the compression
space. This oil is injected into the compression space and recovered, cooled, and
recirculated. The lubricating oil has several functions:
• Seal the internal clearances
• Cool the gas (usually air) during compression
• Lubricate the rotors
• Eliminate the need for timing gears
There are versions of the helical lobe rotary compressor that utilize water
injection (rather than oil). The water accomplishes the same purposes as the oil, but
the air delivered by these machines can be oil-free.