Page 142 - Air and gas Drilling Field Guide 3rd Edition
P. 142
5.6 Prime Mover Input Power Requirements 133
147:3
PR ¼ ð100Þ¼ 66:4:
221:9
Entering the abscissa of Figure 5-16 with the power ratio percent, the approxi-
mate fuel consumption rate can be read on the ordinate using the diesel fuel
curve. The approximate fuel consumption rate at this power level is 3.281 N/
kW-hr. The total weight of diesel fuel consumption per hour is
_ w f ¼ 3:281ð147:3Þ¼ 483:3N=hr:
The specific gravity of diesel fuel is 0.8156, thus the total volume (in U.S. gallons)
of diesel fuel consumption per hour is
483:3
q f ¼ ¼ 60:4 liters=hr:
ð0:8156Þð9:81Þ
Summary
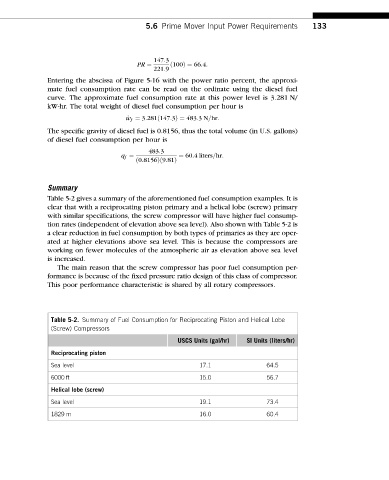
Table 5-2 gives a summary of the aforementioned fuel consumption examples. It is
clear that with a reciprocating piston primary and a helical lobe (screw) primary
with similar specifications, the screw compressor will have higher fuel consump-
tion rates (independent of elevation above sea level). Also shown with Table 5-2 is
a clear reduction in fuel consumption by both types of primaries as they are oper-
ated at higher elevations above sea level. This is because the compressors are
working on fewer molecules of the atmospheric air as elevation above sea level
is increased.
The main reason that the screw compressor has poor fuel consumption per-
formance is because of the fixed pressure ratio design of this class of compressor.
This poor performance characteristic is shared by all rotary compressors.
Table 5-2. Summary of Fuel Consumption for Reciprocating Piston and Helical Lobe
(Screw) Compressors
USCS Units (gal/hr) SI Units (liters/hr)
Reciprocating piston
Sea level 17.1 64.5
6000 ft 15.0 56.7
Helical lobe (screw)
Sea level 19.1 73.4
1829 m 16.0 60.4