Page 458 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 458
Problems 439
Ans. Pi = -P6 = 1200N, P2 = -P5 = 2424N, P3 = -P4 = 2462N,
q12 = q56 = 3.74N/mm7 q23 = q45 = 3.11 N/mm, q340 = 0.06N/mm,
q43i = 12.16N/m11; q52 = 14.58 N/mm, 961 = 11.22 N/mm
P.10.14 Solve P. 10.8 using the method of successive approximations.
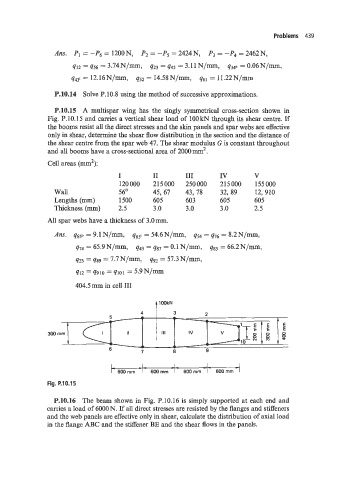
P.10.15 A multispar wing has the singly symmetrical cross-section shown in
Fig. P.10.15 and carries a vertical shear load of 100 kN through its shear centre. If
the booms resist all the direct stresses and the skin panels and spar webs are effective
only in shear: determine the shear flow distribution in the section and the distance of
the shear centre from the spar web 47. The shear modulus G is constant throughout
and all booms have a cross-sectional area of 2000 mm2.
Cell areas (mm2):
I I1 I11 IV V
120000 215000 250000 215000 155000
Wall 56' 45,67 43,78 32,89 12,910
Lengths (mm) 1500 605 603 605 605
Thickness (mm) 2.5 3 .O 3 .O 3 .O 2.5
All spar webs have a thickness of 3.0mm.
zh. q650 = 9.1 N/m, q65' = 54.6N/m11, q54 = q76 = 8.2N/~nm,
q74 = 65.9 N/mm, q43 = qs7 = 0.1 N/mm, qS3 = 66.2 N/mm,
q23 = qsg = 7.7 N/mm, q92 = 57.3 N/m,
q12 = q910 = qlol = 5.9N/mm
404.5 mm in cell I11
lOOkN
300 mm
Fig. P.10.15
P.10.16 The beam shown in Fig. P.10.16 is simply supported at each end and
carries a load of 6000 N. If all direct stresses are resisted by the flanges and stiffeners
and the web panels are effective only in shear, calculate the distribution of axial load
in the flange ABC and the stiffener BE and the shear flows in the panels.