Page 274 - Alternative Energy Systems in Building Design
P. 274
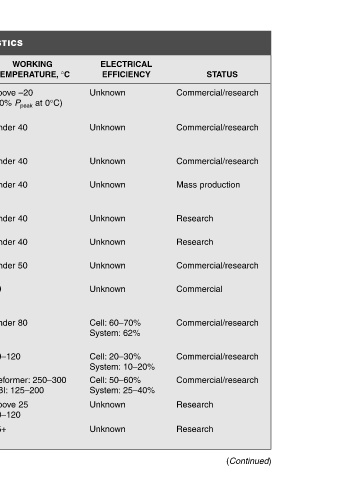
Commercial/research Commercial/research Commercial/research Mass production Research Research Commercial/research Commercial Commercial/research Commercial/research Commercial/research Research Research
STATUS (Continued)
ELECTRICAL EFFICIENCY Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown 60–70% Cell: 62% System: 20–30% Cell: 10–20% System: 50–60% Cell: 25–40% System: Unknown Unknown
°C 250–300
WORKING TEMPERATURE, Above –20 at 0°C) (50% P peak Under 40 Under 40 Under 40 Under 40 Under 40 Under 50 70 Under 80 90–120 Reformer: 125–200 PBI: Above 25 90–120 25+
TYPES OF FUEL CELLS AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS
QUALIFIED POWER Unknown Unknown To 50 W Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown 10–100 kW 100 kW to 1 MW 5 W to 100 kW Up to 140 mW/cm 2 Unknown
ELECTROLYTE Aqueous alkaline solution (e.g., potassium hydroxide) Aqueous alkaline solution (e.g., potassium hydroxide) Polymer membrane (ionomer) Aqueous alkaline solution (e.g., potassium hydroxide) Polymer membrane or humic acid Unknown Polymer membrane (ionomer) Aqueous alkaline solution (e.g., sodium hydroxide) Aqueous alkali
TABLE 7.1 FUEL CELL NAME Metal hydride fuel cell Electrogalvanic fuel cell Direct formic acid fuel cell (DFAFC) Zinc-air battery Microbial fuel cell Upflow microbial fuel cell (UMFC) Reversible fuel cell Direct borohydride fuel cell Alkaline fuel cell Direct methanol fuel cell Reformed methanol fuel cell Direct ethanol fuel cell Dir
249