Page 276 - Alternative Energy Systems in Building Design
P. 276
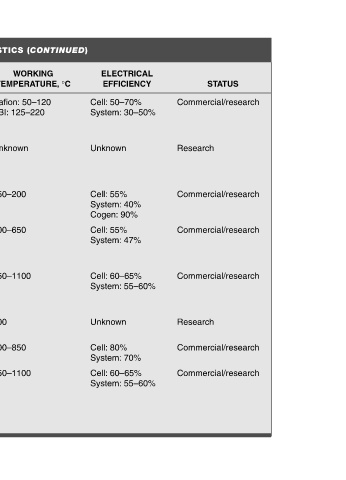
Commercial/research Research Commercial/research Commercial/research Commercial/research Research Commercial/research Commercial/research
STATUS
ELECTRICAL EFFICIENCY 50–70% 30–50% 55% 40% 90% 55% 47% 60–65% 55–60% 80% 70% 60–65% 55–60%
Cell: System: Unknown Cell: System: Cogen: Cell: System: Cell: System: Unknown Cell: System: Cell: System:
TYPES OF FUEL CELLS AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
°C
WORKING TEMPERATURE, 50–120 Nafion: 125–220 PBI: Unknown 150–200 600–650 850–1100 700 700–850 850–1100
QUALIFIED POWER 100 W to kW 500 1 kW to 10 MW Up to 10 MW 100 MW Up to 100 MW Unknown Unknown Up to 100 MW
ELECTROLYTE Polymer membrane (e.g., (ionomer) Nafion or Polybenzimidazole Liquid electrolytes with redox shuttle and polymer membrane (ionomer) Molten phosphoric acid (H 3 PO 4 ) Molten alkaline carbonate (e.g., sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO 3 ) O 2– -conducting ceramic oxide (e.g., zirconium dioxide, ZrO 2 ) H + -conducting cera
TABLE 7.1 FUEL CELL NAME Proton-exchange- membrane fuel cell RFC redox Phosphoric acid fuel cell Molten carbonate fuel cell Tubular solid oxide fuel cell (TSOFC) Protonic ceramic fuel cell Direct carbon fuel cell Planar solid oxide fuel cell Wikipedia. Source:
250