Page 262 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 262
Thermohydromechanical behaviour of soils and soil structure interfaces 237
material for subsequent mechanical loading is independent of temperature (Di Donna
and Laloui, 2013). Key compressibility parameters are the compression index, C c , the
recompression index, C r , and the swelling index, C s . These parameters can be deter-
mined from the relationship between the mean effective stress (in logarithmic scale)
and the void ratio. The slope of the NCL coincides with the value of C c . By consider-
ing that this line is parallel to the critical state line (CSL), considerations about the crit-
ical state can also be performed through the value of C c .
The slope of the compression line seems to be essentially independent of tempera-
ture (Finn, 1951; Campanella and Mitchell, 1968; Despax, 1976; Graham et al., 2001;
Laloui and Cekerevac, 2003). Only a few contradictory experimental results show
nonparallel consolidation curves at different temperatures (Plum and Esrig, 1969;
Sultan et al., 2002). Similarly, the recompression index, C r , and the swelling index,
C s , appear to be insensitive to temperature variations (Di Donna and Laloui, 2013).
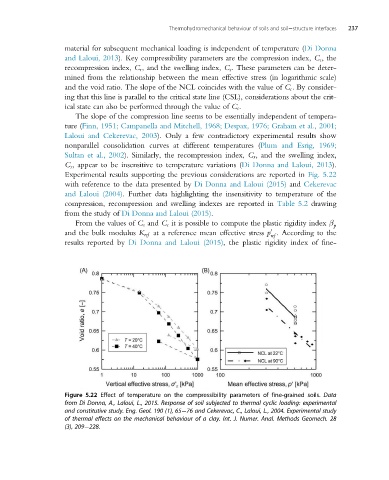
Experimental results supporting the previous considerations are reported in Fig. 5.22
with reference to the data presented by Di Donna and Laloui (2015) and Cekerevac
and Laloui (2004). Further data highlighting the insensitivity to temperature of the
compression, recompression and swelling indexes are reported in Table 5.2 drawing
from the study of Di Donna and Laloui (2015).
From the values of C s and C c it is possible to compute the plastic rigidity index β
p
0
and the bulk modulus K ref at a reference mean effective stress p . According to the
ref
results reported by Di Donna and Laloui (2015), the plastic rigidity index of fine-
Figure 5.22 Effect of temperature on the compressibility parameters of fine-grained soils. Data
from Di Donna, A., Laloui, L., 2015. Response of soil subjected to thermal cyclic loading: experimental
and constitutive study. Eng. Geol. 190 (1), 65 76 and Cekerevac, C., Laloui, L., 2004. Experimental study
of thermal effects on the mechanical behaviour of a clay. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 28
(3), 209 228.