Page 264 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 264
Thermohydromechanical behaviour of soils and soil structure interfaces 239
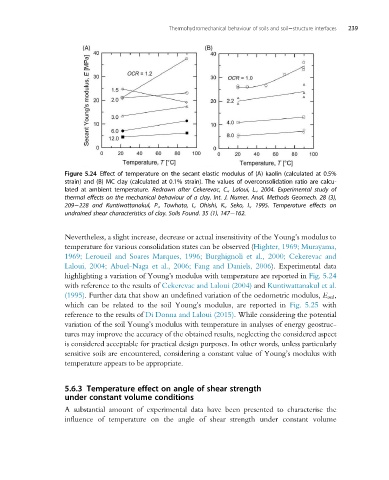
Figure 5.24 Effect of temperature on the secant elastic modulus of (A) kaolin (calculated at 0.5%
strain) and (B) MC clay (calculated at 0.1% strain). The values of overconsolidation ratio are calcu-
lated at ambient temperature. Redrawn after Cekerevac, C., Laloui, L., 2004. Experimental study of
thermal effects on the mechanical behaviour of a clay. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 28 (3),
209 228 and Kuntiwattanakul, P., Towhata, I., Ohishi, K., Seko, I., 1995. Temperature effects on
undrained shear characteristics of clay. Soils Found. 35 (1), 147 162.
Nevertheless, a slight increase, decrease or actual insensitivity of the Young’s modulus to
temperature for various consolidation states can be observed (Highter, 1969; Murayama,
1969; Leroueil and Soares Marques, 1996; Burghignoli et al., 2000; Cekerevac and
Laloui, 2004; Abuel-Naga et al., 2006; Fang and Daniels, 2006). Experimental data
highlighting a variation of Young’s modulus with temperature are reported in Fig. 5.24
with reference to the results of Cekerevac and Laloui (2004) and Kuntiwattanakul et al.
(1995). Further data that show an undefined variation of the oedometric modulus, E oed ,
which can be related to the soil Young’s modulus, are reported in Fig. 5.25 with
reference to the results of Di Donna and Laloui (2015). While considering the potential
variation of the soil Young’s modulus with temperature in analyses of energy geostruc-
tures may improve the accuracy of the obtained results, neglecting the considered aspect
is considered acceptable for practical design purposes. In other words, unless particularly
sensitive soils are encountered, considering a constant value of Young’s modulus with
temperature appears to be appropriate.
5.6.3 Temperature effect on angle of shear strength
under constant volume conditions
A substantial amount of experimental data have been presented to characterise the
influence of temperature on the angle of shear strength under constant volume