Page 261 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 261
236 Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
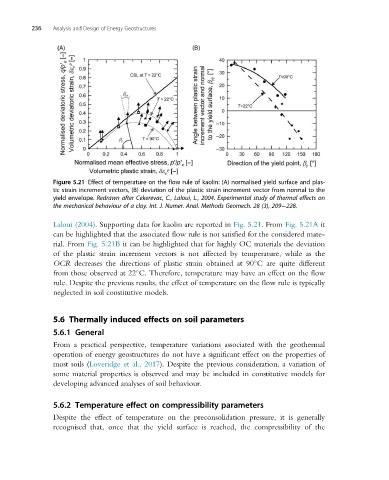
Figure 5.21 Effect of temperature on the flow rule of kaolin: (A) normalised yield surface and plas-
tic strain increment vectors, (B) deviation of the plastic strain increment vector from normal to the
yield envelope. Redrawn after Cekerevac, C., Laloui, L., 2004. Experimental study of thermal effects on
the mechanical behaviour of a clay. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 28 (3), 209 228.
Laloui (2004). Supporting data for kaolin are reported in Fig. 5.21. From Fig. 5.21A it
can be highlighted that the associated flow rule is not satisfied for the considered mate-
rial. From Fig. 5.21B it can be highlighted that for highly OC materials the deviation
of the plastic strain increment vectors is not affected by temperature, while as the
OCR decreases the directions of plastic strain obtained at 90 C are quite different
from those observed at 22 C. Therefore, temperature may have an effect on the flow
rule. Despite the previous results, the effect of temperature on the flow rule is typically
neglected in soil constitutive models.
5.6 Thermally induced effects on soil parameters
5.6.1 General
From a practical perspective, temperature variations associated with the geothermal
operation of energy geostructures do not have a significant effect on the properties of
most soils (Loveridge et al., 2017). Despite the previous consideration, a variation of
some material properties is observed and may be included in constitutive models for
developing advanced analyses of soil behaviour.
5.6.2 Temperature effect on compressibility parameters
Despite the effect of temperature on the preconsolidation pressure, it is generally
recognised that, once that the yield surface is reached, the compressibility of the