Page 256 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 256
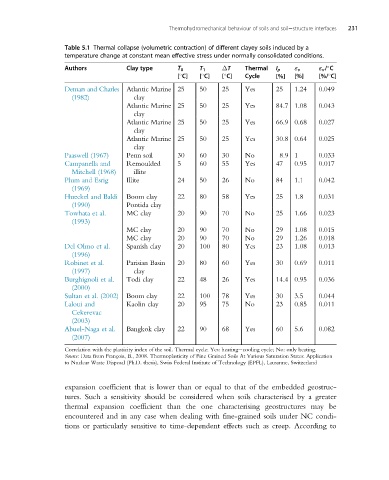
Thermohydromechanical behaviour of soils and soil structure interfaces 231
Table 5.1 Thermal collapse (volumetric contraction) of different clayey soils induced by a
temperature change at constant mean effective stress under normally consolidated conditions.
Authors Clay type T 0 T 1 ΔT Thermal I p ε v ε v / C
[ C] [ C] [ C] Cycle [%] [%] [%/ C]
Demars and Charles Atlantic Marine 25 50 25 Yes 25 1.24 0.049
(1982) clay
Atlantic Marine 25 50 25 Yes 84.7 1.08 0.043
clay
Atlantic Marine 25 50 25 Yes 66.9 0.68 0.027
clay
Atlantic Marine 25 50 25 Yes 30.8 0.64 0.025
clay
Paaswell (1967) Penn soil 30 60 30 No 8.9 1 0.033
Campanella and Remoulded 5 60 55 Yes 47 0.95 0.017
Mitchell (1968) illite
Plum and Esrig Illite 24 50 26 No 84 1.1 0.042
(1969)
Hueckel and Baldi Boom clay 22 80 58 Yes 25 1.8 0.031
(1990) Pontida clay
Towhata et al. MC clay 20 90 70 No 25 1.66 0.023
(1993)
MC clay 20 90 70 No 29 1.08 0.015
MC clay 20 90 70 No 29 1.26 0.018
Del Olmo et al. Spanish clay 20 100 80 Yes 23 1.08 0.013
(1996)
Robinet et al. Parisian Basin 20 80 60 Yes 30 0.69 0.011
(1997) clay
Burghignoli et al. Todi clay 22 48 26 Yes 14.4 0.95 0.036
(2000)
Sultan et al. (2002) Boom clay 22 100 78 Yes 30 3.5 0.044
Laloui and Kaolin clay 20 95 75 No 23 0.85 0.011
Cekerevac
(2003)
Abuel-Naga et al. Bangkok clay 22 90 68 Yes 60 5.6 0.082
(2007)
Correlation with the plasticity index of the soil. Thermal cycle: Yes: heating cooling cycle; No: only heating.
Source: Data from François, B., 2008. Thermoplasticity of Fine Grained Soils At Various Saturation States: Application
to Nuclear Waste Disposal (Ph.D. thesis), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
expansion coefficient that is lower than or equal to that of the embedded geostruc-
tures. Such a sensitivity should be considered when soils characterised by a greater
thermal expansion coefficient than the one characterising geostructures may be
encountered and in any case when dealing with fine-grained soils under NC condi-
tions or particularly sensitive to time-dependent effects such as creep. According to