Page 252 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 252
Thermohydromechanical behaviour of soils and soil structure interfaces 227
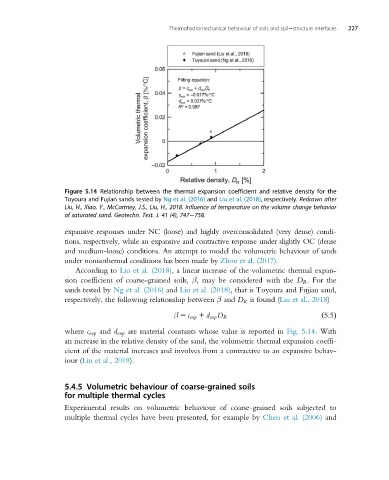
Figure 5.14 Relationship between the thermal expansion coefficient and relative density for the
Toyoura and Fujian sands tested by Ng et al. (2016) and Liu et al. (2018), respectively. Redrawn after
Liu, H., Xiao, Y., McCartney, J.S., Liu, H., 2018. Influence of temperature on the volume change behavior
of saturated sand. Geotechn. Test. J. 41 (4), 747 758.
expansive responses under NC (loose) and highly overconsolidated (very dense) condi-
tions, respectively, while an expansive and contractive response under slightly OC (dense
and medium-loose) conditions. An attempt to model the volumetric behaviour of sands
under nonisothermal conditions has been made by Zhou et al. (2017).
According to Liu et al. (2018), a linear increase of the volumetric thermal expan-
sion coefficient of coarse-grained soils, β, may be considered with the D R . For the
sands tested by Ng et al. (2016) and Liu et al. (2018), that is Toyoura and Fujian sand,
respectively, the following relationship between β and D R is found (Liu et al., 2018)
ð5:5Þ
β 5 c exp 1 d exp D R
where c exp and d exp are material constants whose value is reported in Fig. 5.14. With
an increase in the relative density of the sand, the volumetric thermal expansion coeffi-
cient of the material increases and involves from a contractive to an expansive behav-
iour (Liu et al., 2018).
5.4.5 Volumetric behaviour of coarse-grained soils
for multiple thermal cycles
Experimental results on volumetric behaviour of coarse-grained soils subjected to
multiple thermal cycles have been presented, for example by Chen et al. (2006) and