Page 40 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 40
Energy and geotechnologies 9
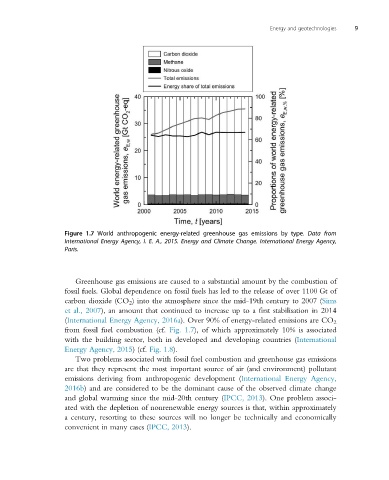
Figure 1.7 World anthropogenic energy-related greenhouse gas emissions by type. Data from
International Energy Agency, I. E. A., 2015. Energy and Climate Change. International Energy Agency,
Paris.
Greenhouse gas emissions are caused to a substantial amount by the combustion of
fossil fuels. Global dependence on fossil fuels has led to the release of over 1100 Gt of
carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into the atmosphere since the mid-19th century to 2007 (Sims
et al., 2007), an amount that continued to increase up to a first stabilisation in 2014
(International Energy Agency, 2016a). Over 90% of energy-related emissions are CO 2
from fossil fuel combustion (cf. Fig. 1.7), of which approximately 10% is associated
with the building sector, both in developed and developing countries (International
Energy Agency, 2015) (cf. Fig. 1.8).
Two problems associated with fossil fuel combustion and greenhouse gas emissions
are that they represent the most important source of air (and environment) pollutant
emissions deriving from anthropogenic development (International Energy Agency,
2016b) and are considered to be the dominant cause of the observed climate change
and global warming since the mid-20th century (IPCC, 2013). One problem associ-
ated with the depletion of nonrenewable energy sources is that, within approximately
a century, resorting to these sources will no longer be technically and economically
convenient in many cases (IPCC, 2013).