Page 145 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 145
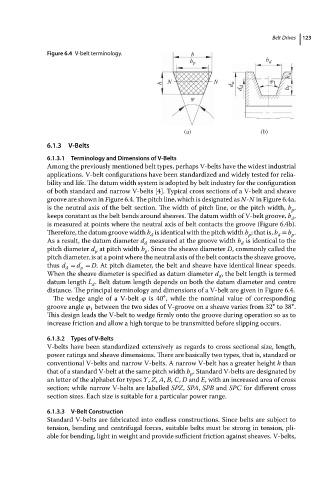
Figure 6.4 V-belt terminology. b Belt Drives 123
b p b d
h a
h N N d a φ 1
d d h f
φ
(a) (b)
6.1.3 V-Belts
6.1.3.1 Terminology and Dimensions of V-Belts
Among the previously mentioned belt types, perhaps V-belts have the widest industrial
applications. V-belt configurations have been standardized and widely tested for relia-
bility and life. The datum width system is adopted by belt industry for the configuration
of both standard and narrow V-belts [4]. Typical cross sections of a V-belt and sheave
groove are shown in Figure 6.4. The pitch line, which is designated as N-N in Figure 6.4a,
is the neutral axis of the belt section. The width of pitch line, or the pitch width, b ,
p
keeps constant as the belt bends around sheaves. The datum width of V-belt groove, b ,
d
is measured at points where the neutral axis of belt contacts the groove (Figure 6.4b).
Therefore, the datum groove width b is identical with the pitch width b ;thatis, b = b .
p
p
d
d
As a result, the datum diameter d measured at the groove width b is identical to the
d d
pitch diameter d at pitch width b . Since the sheave diameter D, commonly called the
p p
pitch diameter, is at a point where the neutral axis of the belt contacts the sheave groove,
thus d = d = D. At pitch diameter, the belt and sheave have identical linear speeds.
p
d
When the sheave diameter is specified as datum diameter d , the belt length is termed
d
datum length L . Belt datum length depends on both the datum diameter and centre
d
distance. The principal terminology and dimensions of a V-belt are given in Figure 6.4.
∘
The wedge angle of a V-belt is 40 , while the nominal value of corresponding
∘
∘
groove angle between the two sides of V-groove on a sheave varies from 32 to 38 .
1
Thisdesignleads theV-belttowedge firmlyontothe groove during operationsoasto
increase friction and allow a high torque to be transmitted before slipping occurs.
6.1.3.2 Types of V-Belts
V-belts have been standardized extensively as regards to cross sectional size, length,
power ratings and sheave dimensions. There are basically two types, that is, standard or
conventional V-belts and narrow V-belts. A narrow V-belt has a greater height h than
that of a standard V-belt at the same pitch width b . Standard V-belts are designated by
p
an letter of the alphabet for types Y, Z, A, B, C, D and E, with an increased area of cross
section; while narrow V-belts are labelled SPZ, SPA, SPB and SPC for different cross
section sizes. Each size is suitable for a particular power range.
6.1.3.3 V-Belt Construction
Standard V-belts are fabricated into endless constructions. Since belts are subject to
tension, bending and centrifugal forces, suitable belts must be strong in tension, pli-
able for bending, light in weight and provide sufficient friction against sheaves. V-belts,