Page 315 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 315
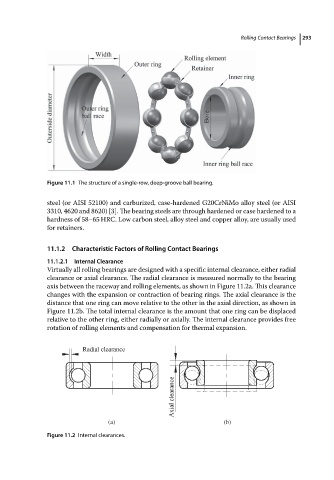
Figure 11.1 The structure of a single-row, deep-groove ball bearing. Rolling Contact Bearings 293
steel (or AISI 52100) and carburized, case-hardened G20CrNiMo alloy steel (or AISI
3310, 4620 and 8620) [3]. The bearing steels are through hardened or case hardened to a
hardness of 58–65 HRC. Low carbon steel, alloy steel and copper alloy, are usually used
for retainers.
11.1.2 Characteristic Factors of Rolling Contact Bearings
11.1.2.1 Internal Clearance
Virtually all rolling bearings are designed with a specific internal clearance, either radial
clearance or axial clearance. The radial clearance is measured normally to the bearing
axis between the raceway and rolling elements, as shown in Figure 11.2a. This clearance
changes with the expansion or contraction of bearing rings. The axial clearance is the
distance that one ring can move relative to the other in the axial direction, as shown in
Figure 11.2b. The total internal clearance is the amount that one ring can be displaced
relative to the other ring, either radially or axially. The internal clearance provides free
rotation of rolling elements and compensation for thermal expansion.
(a) (b)
Figure 11.2 Internal clearances.