Page 373 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 373
(5) Nonmetallic materials Sliding Bearings 351
Nonmetallic bearing materials mainly refer to various plastic materials, including,
fiuoropolymers, phenolics, polycarbonates, acetals, nylons, Teflon and many others
[3]. They have inherently low coefficient of friction against metal surfaces, and offer
the possibility of dry running or with a very limited supply of lubricant. Many of
them have low strength, low melting point and poor thermal conduction, which
severely limits the load carrying capacity and operating speed. Therefore, plastic
bearings are widely used for low to moderate loads and speeds. They are lightweight,
easy to machine and inexpensive. Other nonmetallic materials for bearings include
graphite, rubber, woods and so on [13].
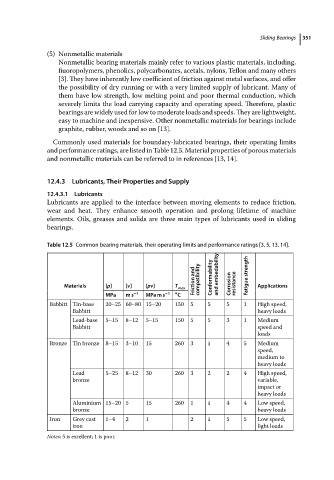
Commonly used materials for boundary-lubricated bearings, their operating limits
and performance ratings, are listed in Table 12.5. Material properties of porous materials
and nonmetallic materials can be referred to in references [13, 14].
12.4.3 Lubricants, Their Properties and Supply
12.4.3.1 Lubricants
Lubricants are applied to the interface between moving elements to reduce friction,
wear and heat. They enhance smooth operation and prolong lifetime of machine
elements. Oils, greases and solids are three main types of lubricants used in sliding
bearings.
Table 12.5 Common bearing materials, their operating limits and performance ratings [3, 5, 13, 14].
Friction and compatibility Conformability and embedability Fatigue strength
Materials [p] [v] [pv] T max Corrosion resistance Applications
MPa ms −1 MPa m s −1 ∘ C
Babbitt Tin-base 20–25 60–80 15–20 150 5 5 5 1 High speed,
Babbitt heavy loads
Lead-base 5–15 8–12 5–15 150 5 5 3 1 Medium
Babbitt speed and
loads
Bronze Tin bronze 8–15 3–10 15 260 3 1 4 5 Medium
speed,
medium to
heavy loads
Lead 5–25 8–12 30 260 3 2 2 4 High speed,
bronze variable,
impact or
heavy loads
Aluminium 15–20 5 15 260 1 1 4 4 Low speed,
bronze heavy loads
Iron Grey cast 1–4 2 1 2 1 5 5 Low speed,
iron light loads
Notes: 5 is excellent; 1 is poor.