Page 84 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 84
Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
62
p
p 2
8
60˚ p
0.54p 2
p p
4
p d 1
d 1 d 2
d 2
d d
(a) (b)
29˚ 0.163p 7˚
p 45˚
2
p 0.663p
2
p
p
d 1 d 1
d 2 d 2 d
d
(c) (d)
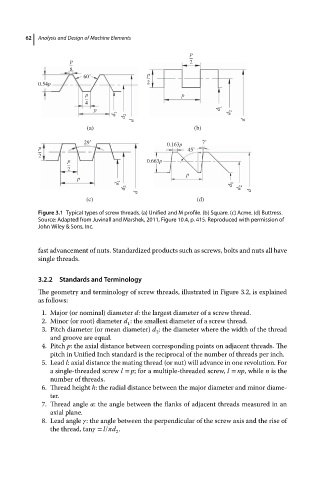
Figure 3.1 Typical types of screw threads. (a) Unified and M profile. (b) Square. (c) Acme. (d) Buttress.
Source: Adapted from Juvinall and Marshek, 2011, Figure 10.4, p. 415. Reproduced with permission of
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
fast advancement of nuts. Standardized products such as screws, bolts and nuts all have
single threads.
3.2.2 Standards and Terminology
The geometry and terminology of screw threads, illustrated in Figure 3.2, is explained
as follows:
1. Major (or nominal) diameter d: the largest diameter of a screw thread.
2. Minor (or root) diameter d : the smallest diameter of a screw thread.
1
3. Pitch diameter (or mean diameter) d : the diameter where the width of the thread
2
and groove are equal.
4. Pitch p: the axial distance between corresponding points on adjacent threads. The
pitch in Unified Inch standard is the reciprocal of the number of threads per inch.
5. Lead l: axial distance the mating thread (or nut) will advance in one revolution. For
a single-threaded screw l = p; for a multiple-threaded screw, l = np, while n is the
number of threads.
6. Thread height h: the radial distance between the major diameter and minor diame-
ter.
7. Thread angle : the angle between the flanks of adjacent threads measured in an
axial plane.
8. Lead angle : the angle between the perpendicular of the screw axis and the rise of
the thread, tan = l/ d .
2