Page 88 - Analysis, Synthesis and Design of Chemical Processes, Third Edition
P. 88
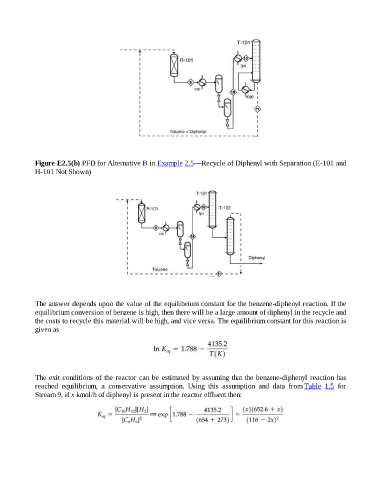
Figure E2.5(b) PFD for Alternative B in Example 2.5—Recycle of Diphenyl with Separation (E-101 and
H-101 Not Shown)
The answer depends upon the value of the equilibrium constant for the benzene-diphenyl reaction. If the
equilibrium conversion of benzene is high, then there will be a large amount of diphenyl in the recycle and
the costs to recycle this material will be high, and vice versa. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is
given as
The exit conditions of the reactor can be estimated by assuming that the benzene-diphenyl reaction has
reached equilibrium, a conservative assumption. Using this assumption and data from Table 1.5 for
Stream 9, if x kmol/h of diphenyl is present in the reactor effluent then: