Page 324 - Analytical method for food addtives
P. 324
218
Reference
1
2
FID at 250 ºC
RI at 40 ºC
Detection
Separated on HPLC column: Shodex SUGAR SC1011 at
methanolic KOH. Fatty acids (lauric and myristic acids)
GC Column: 6′ × 0.125″ glass column packed with 3 %
were acidified, extracted with diethyl ether, methylated
50 ºC with water–acetonitrile (985:15) mobile phase at
SPE using a silica cartridge and hydrolysis of sorbitan
OV-17 on 80/100 mesh Chromosorb W. Isothermal at
Extracted into diethyl ether and saponified with
tristearate (STS) [E492] to sorbitol.
0.8 mL/min and 50 µL injection
using ethereal dizomethane.
205 ºC, 1 µL injection
Extraction Analytical methods for food additives 3 Extract purified by silica gel column chromatography. Polar substances were washed out with ether–chloroform (1:99), then isosorbide monoesters were eluted with methanol–chloroform (5:95) and sorbitan monoesters were eluted with methanol. These separated emulsifiers were convert
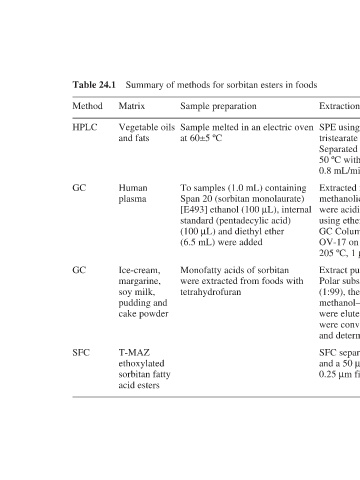
Summary of methods for sorbitan esters in foods
Sample preparation Sample melted in an electric oven at 60±5 ºC To samples (1.0 mL) containing Span 20 (sorbitan monolaurate) [E493] ethanol (100 µL), internal standard (pentadecylic acid) (100 µL) and diethyl ether (6.5 mL) were added Monofatty acids of sorbitan were extracted from foods with tetrahydrofuran
Vegetable oils Ice-cream, margarine, pudding and cake powder ethoxylated sorbitan fatty acid esters
Matrix and fats Human plasma soy milk, T-MAZ
Table 24.1 Method HPLC GC GC SFC