Page 263 - Antennas for Base Stations in Wireless Communications
P. 263
236 Chapter Six
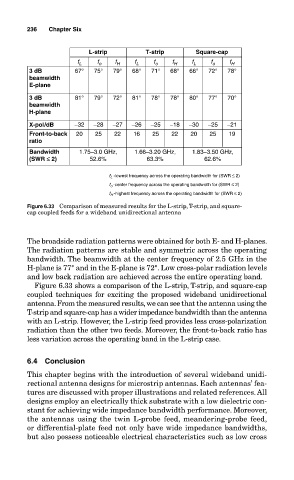
L-strip T-strip Square-cap
f L f o f H f L f o f H f L f o f H
3 dB 67° 75° 79° 68° 71° 68° 66° 72° 78°
beamwidth
E-plane
3 dB 81° 79° 72° 81° 78° 78° 80° 77° 70°
beamwidth
H-plane
X-pol/dB −32 −28 −27 −26 −25 −18 −30 −25 −21
Front-to-back 20 25 22 16 25 22 20 25 19
ratio
Bandwidth 1.75–3.0 GHz, 1.66–3.20 GHz, 1.83–3.50 GHz,
(SWR Ä 2) 52.6% 63.3% 62.6%
f L -lowest frequency across the operating bandwidth for (SWR ≤ 2)
f o -center frequency across the operating bandwidth for (SWR ≤ 2)
f H -highest frequency across the operating bandwidth for (SWR ≤ 2)
Figure 6.33 Comparison of measured results for the L-strip, T-strip, and square-
cap coupled feeds for a wideband unidirectional antenna
The broadside radiation patterns were obtained for both E- and H-planes.
The radiation patterns are stable and symmetric across the operating
bandwidth. The beamwidth at the center frequency of 2.5 GHz in the
H-plane is 77° and in the E-plane is 72°. Low cross-polar radiation levels
and low back radiation are achieved across the entire operating band.
Figure 6.33 shows a comparison of the L-strip, T-strip, and square-cap
coupled techniques for exciting the proposed wideband unidirectional
antenna. From the measured results, we can see that the antenna using the
T-strip and square-cap has a wider impedance bandwidth than the antenna
with an L-strip. However, the L-strip feed provides less cross-polarization
radiation than the other two feeds. Moreover, the front-to-back ratio has
less variation across the operating band in the L-strip case.
6.4 Conclusion
This chapter begins with the introduction of several wideband unidi-
rectional antenna designs for microstrip antennas. Each antennas’ fea-
tures are discussed with proper illustrations and related references. All
designs employ an electrically thick substrate with a low dielectric con-
stant for achieving wide impedance bandwidth performance. Moreover,
the antennas using the twin L-probe feed, meandering-probe feed,
or differential-plate feed not only have wide impedance bandwidths,
but also possess noticeable electrical characteristics such as low cross