Page 350 - Anthropometry, Apparel Sizing and Design
P. 350
Sizing and fit for pressure garments 343
CP ¼ P warp + P weft = E warp + E weft , (13.2)
where CP is the compression index reflecting the ability of elongated knitted materials
to create pressure, kPa/%; P is the pressure measured between the soft tissue of the
human body and the elongated materials in warp and weft directions, kPa; E is the
elongation of knitted materials in warp and weft directions or the design ease allow-
ance in pattern block of a pressure garment, %.
The higher the value of CP, the stronger is the pressure performance of the knitted
materials. The lower the value of CP, the weaker the knitted materials’ pressure per-
formance. For example, if CP is 0.13kPa/%, the materials can provide 0.13kPa to the
soft tissue of the body when we decrease the length of sample or increase the negative
ease allowance of the pattern block by 1%; when the waist girth is 80cm, we should
decrease the width of the pattern block by 10% to get the new value of 72cm. The
designed garment will provide a pressure of 1.30kPa in the waist area.
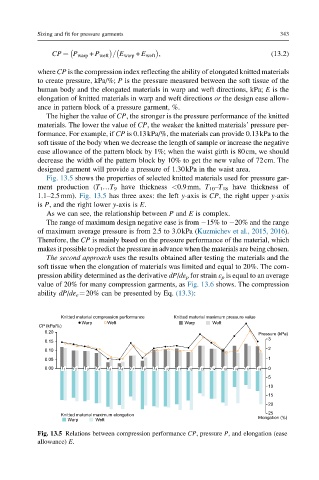
Fig. 13.5 shows the properties of selected knitted materials used for pressure gar-
ment production (T 1 …T 9 have thickness <0.9mm, T 10 –T 18 have thickness of
1.1–2.5mm). Fig. 13.5 has three axes: the left y-axis is CP, the right upper y-axis
is P, and the right lower y-axis is E.
As we can see, the relationship between P and E is complex.
The range of maximum design negative ease is from 15% to 20% and the range
of maximum average pressure is from 2.5 to 3.0kPa (Kuzmichev et al., 2015, 2016).
Therefore, the CP is mainly based on the pressure performance of the material, which
makes it possible to predict the pressure in advance when the materials are being chosen.
The second approach uses the results obtained after testing the materials and the
soft tissue when the elongation of materials was limited and equal to 20%. The com-
pression ability determined as the derivative dP/dε p for strain ε p is equal to an average
value of 20% for many compression garments, as Fig. 13.6 shows. The compression
ability dP/dε ε ¼20% can be presented by Eq. (13.3):
Knitted material compression performance Knitted material maximum pressure value
Warp Weft Warp Weft
CP (kPa/%)
0.20
Pressure (kPa)
3
0.15
0.10 2
0.05 1
0.00 T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 T 5 T 6 T 7 T 8 T 9 T 10 T 11 T 12 T 13 T 14 T 15 T 16 T 17 T 18 0
5
10
15
20
25
Knitted material maximum elongation Elongation (%)
Warp Weft
Fig. 13.5 Relations between compression performance CP, pressure P, and elongation (ease
allowance) E.