Page 246 - Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
P. 246
240 Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
Gradient (SG)
1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
0
500 Lithostatic gradient
1000 Fracture
Depth TVD (m) 1500 gradient Casing
2000
2500
3000 Mud weight
Pore pressure
3500 gradient
4000
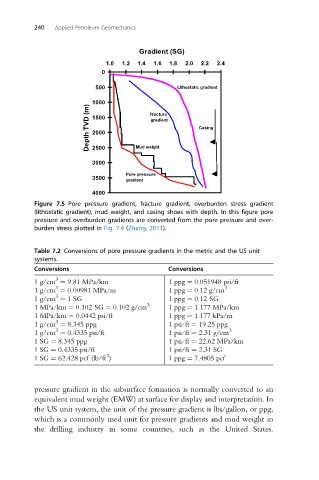
Figure 7.5 Pore pressure gradient, fracture gradient, overburden stress gradient
(lithostatic gradient), mud weight, and casing shoes with depth. In this figure pore
pressure and overburden gradients are converted from the pore pressure and over-
burden stress plotted in Fig. 7.4 (Zhang, 2011).
Table 7.2 Conversions of pore pressure gradients in the metric and the US unit
systems.
Conversions Conversions
3
1 g/cm ¼ 9.81 MPa/km 1 ppg ¼ 0.051948 psi/ft
3
1 g/cm ¼ 0.00981 MPa/m 1 ppg ¼ 0.12 g/cm 3
3
1 g/cm ¼ 1 SG 1 ppg ¼ 0.12 SG
1 MPa/km ¼ 0.102 SG ¼ 0.102 g/cm 3 1 ppg ¼ 1.177 MPa/km
1 MPa/km ¼ 0.0442 psi/ft 1 ppg ¼ 1.177 kPa/m
3
1 g/cm ¼ 8.345 ppg 1 psi/ft ¼ 19.25 ppg
3
1 g/cm ¼ 0.4335 psi/ft 1 psi/ft ¼ 2.31 g/cm 3
1SG ¼ 8.345 ppg 1 psi/ft ¼ 22.62 MPa/km
1SG ¼ 0.4335 psi/ft 1 psi/ft ¼ 2.31 SG
3
1SG ¼ 62.428 pcf (lb/ft ) 1 ppg ¼ 7.4805 pcf
pressure gradient in the subsurface formation is normally converted to an
equivalent mud weight (EMW) at surface for display and interpretation. In
the US unit system, the unit of the pressure gradient is lbs/gallon, or ppg,
which is a commonly used unit for pressure gradients and mud weight in
the drilling industry in some countries, such as the United States.