Page 98 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 98
84 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
30 psig
I-+ d
I N2pad 1 I
5 psig 70’F-l 200 ft Noi mal operating level
Pressure gauge
c T
Sharp exit a
15R
Storage tank Centrifugal pump Reactor
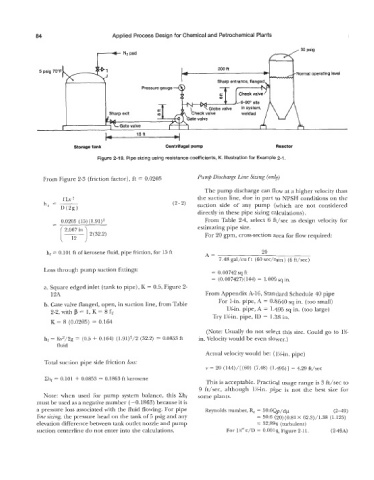
Figure 2-19. Pipe sizing using resistance coefficients, K. Illustration for Example 2-1.
From Figure 2-3 (friction factor), ft = 0.0205 Pump Discharge Line Sizing (only)
The pump discharge can flow at a higher velocity than
the suction line, due in part to NPSH conditions on the
(2- 2) suction side of any pump (which are not considered
directly in these pipe sizing calculations).
(T) estimating pipe size.
- 0.0205 (15) (l.91)z From Table 2-4, select 6 ft/sec as design velocity for
2(32.2)
For 20 gpm, cross-section area for flow required:
hf = 0.101 ft of kerosene fluid, pipe friction, for 15 ft A= 20
7.48 gal/cu f t (60 sec/min ) (6 ft/sec)
Loss through pump suction fittings: = 0.00742 sq ft
= (0.007427)(144) = 1.009 sq in.
a. Square edged inlet (tank to pipe), K = 0.5, Figure 2-
12A From Appendix A-16, Standard Schedule 40 pipe
For 1-in. pipe, A = 0.8640 sq in. (too small)
b. Gate valve flanged, open, in suction line, from Table 1%-in. pipe, A = 1.495 sq in. (too large)
2-2, With p = 1, K = 8 fT
Try 1X-h pipe, ID = 1.38 in.
K = 8 (0.0205) = 0.164
(Note: Usually do not select this size. Could go to 1%-
hf = Kvz/2g = (0.5 f 0.164) (1.91)2/2 (32.2) = 0.0853 ft in. Velocity would be even slower.)
fluid
Actual velocity would be: (1Kin. pipe)
Total suction pipe side friction loss:
v = 20 (144)/[(60) (7.48) (1.495)] = 4.29 ft/sec
Ch, = 0.101 + 0.0853 = 0.1863 ft kerosene
This is acceptable. Practical usage range is 3 ft/sec to
9 ft/sec, although lg-in. pipe is not the best size for
Note: when used for pump system balance, this Xhf some plants.
must be used as a negative number (-0.1863) because it is
a pressure loss associated with the fluid flowing. For pipe Reynolds number, R, = 50.6Qp/dp (2-49)
line sizing, the pressure head on the tank of 5 psig and any = 50.6 (20) (0.81 X 62.3)/1.38 (1.125)
elevation difference between tank outlet nozzle and pump = 32,894 (turbulent)
suction centerline do not enter into the calculations. For 1%’’ &/D = 0.0014, Figure 2-11. (2-49A)