Page 94 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 94
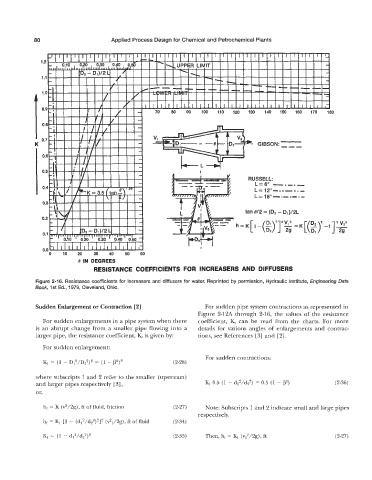
80 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
1 0
K
tan 812 = (D, - D1)/2L
h=
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
e IN DEGREES
RESISTANCE COEFFICIENTS FOR INCREASERS AND DIFFUSERS
Figure 2-16. Resistance coefficients for increasers and diffusers for water. Reprinted by permission, Hydraulic Institute, Engineering Data
Book, 1st Ed., 1979, Cleveland, Ohio.
Sudden Enlargement or Contraction [21 For sudden pipe system contractions as represented in
Figure 2-12A through 2-16, the values of the resistance
For sudden enlargements in a pipe system when there coefficient, K, can be read from the charts. For more
is an abrupt change from a smaller pipe flowing into a details for various angles of enlargements and contrac-
larger pipe, the resistance coefficient, K, is given by: tions, see References [3] and [2].
For sudden enlargement:
K1 = (1 - D1P/D24)* = (1 - p2)' (2-28) For sudden contractions:
where subscripts 1 and 2 refer to the smaller (upstream)
and larger pipes respectively [ 31, K1 0.5 (1 - dl2/d2') = 0.5 (1 - p') (2-36)
0 r,
hf = K (v2/2g), ft of fluid, friction (2-27) Note: Subscripts 1 and 2 indicate small and large pipes
respectively.
hf = Kl [l - (d12/dz')z]z (vZ1,/2g), ft of fluid (2-34)
K1 = (1 - dl'/d~2)z (2-35) Then, h, = K, (v12/2g), ft (2-27)