Page 171 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume II
P. 171
160 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
the cap. When the required opening exceeds the avail-
PL;vPv)]l/z
able, the vapor will either flow under the cap, create Vm=0.79(A,) [ H, ( - (8- 226)
greater pressure drop or both.
A. Caps with Rectangular Slots [60] where A, = total slot area per tray, ft2
H, = slot height, in.
V, = maximum allowable vapor load per tray, ft3/sec
-
(8 225)
B. Caps with Trapezoidal Slots
where h, = slot opening, or pressure drop through slot, in. A trial solution is involved in determining the slot open-
liquid ing for trapezoidal slots [5]. The relation for maximum
V = total vapor flow through tray, ft3/sec capacity at full slot opening is:
Nc = number of caps per tray V,=2.36(As)x[2(- R, +-(- 4 1-Rs) 1
N, = number of slots per cap
w, = width of slot (rectangular), in. 3 ~+R,J 15 1+R,)
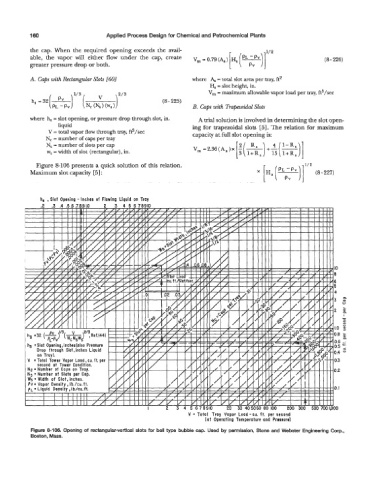
Figure 8-106 presents a quick solution of this relation. 1/2
Maximum slot capacity [5] : [Hs(v)] (8-227)
h, , Slot Opening -Inches of Flowing Liquid on Tray
V = Total Tray Vapor Load - cu. ft. per second
[at Operating Temperature and Pressure)
Figure 8-106. Opening of rectangular-vertical slots for bell type bubble cap. Used by permission, Stone and Webster Engineering Corp.,
Boston, Mass.