Page 223 - Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing
P. 223
214 CHAPTER 10 Computers Versus Brains: Game Is Over or More to Come?
all other nodes of the lattice. Note that in mean field models, the actual lattice
geometry becomes irrelevant due to the all-to-all interactions.
Mesoscopic, or intermediate-range, effects are of particular interest, when a node
interacts with some nodes beyond its immediate neighbors but not the whole lattice.
Intermediate-range coupling can produce peculiar resonance effects when oscillations
emerge in a narrow frequency band. Detailed analysis showed that mesoscopic
coupling produces the so-called chimera effect with the mixture of qualitatively
different behaviors identified, for example, in laser systems [46]. In chimera dy-
namics, the array of identical oscillators splits into two domains: one coherent with
phase synchrony, while the other lacks coherence and is desynchronized. Chimera
states in oscillatory systems of physics are named after mythological beasts with
multiple heads and identities joined in one body [47].
The coexistence of multiple dynamical states in a single system is an important
behavior that bears relevance to many fields of science, including biological and
artificial intelligence. In the case of the CML physical model, the bistable/multistable
dynamics became prominent in the case of mesoscopic coupling, which represents
an intermediate-range effect between the extremes of microscopic and macroscopic
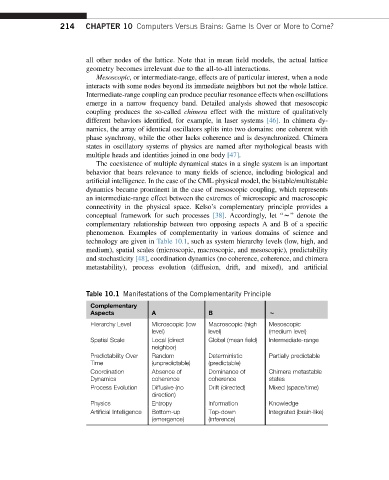
connectivity in the physical space. Kelso’s complementary principle provides a
conceptual framework for such processes [38].Accordingly,let “w”denotethe
complementary relationship between two opposing aspects A and B of a specific
phenomenon. Examples of complementarity in various domains of science and
technology are given in Table 10.1, such as system hierarchy levels (low, high, and
medium), spatial scales (microscopic, macroscopic, and mesoscopic), predictability
and stochasticity [48], coordination dynamics (no coherence, coherence, and chimera
metastability), process evolution (diffusion, drift, and mixed), and artificial
Table 10.1 Manifestations of the Complementarity Principle
Complementary
Aspects A B w
Hierarchy Level Microscopic (low Macroscopic (high Mesoscopic
level) level) (medium level)
Spatial Scale Local (direct Global (mean field) Intermediate-range
neighbor)
Predictability Over Random Deterministic Partially predictable
Time (unpredictable) (predictable)
Coordination Absence of Dominance of Chimera metastable
Dynamics coherence coherence states
Process Evolution Diffusive (no Drift (directed) Mixed (space/time)
direction)
Physics Entropy Information Knowledge
Artificial Intelligence Bottom-up Top-down Integrated (brain-like)
(emergence) (inference)