Page 75 - Assurance of Sterility for Sensitive Combination Products and Materials
P. 75
Aseptic processing 61
transporting utilities should, where possible, be treated to eliminate contam-
ination. Compressed gases, nitrogen, and air should be filtered to remove
microbiological contamination. Electrical power should be uninterrupted.
It is recommended that backup systems be in place to ensure that critical
control operations such as airflow through the HEPA system are not inter-
rupted. Routine monitoring and testing of the utilities and materials should
be performed to confirm the output of the utilities and quality process
materials.
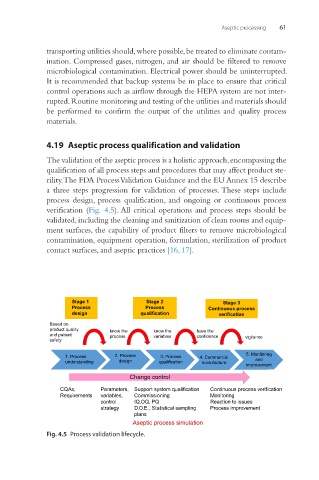
4.19 Aseptic process qualification and validation
The validation of the aseptic process is a holistic approach, encompassing the
qualification of all process steps and procedures that may affect product ste-
rility. The FDA Process Validation Guidance and the EU Annex 15 describe
a three steps progression for validation of processes. These steps include
process design, process qualification, and ongoing or continuous process
verification (Fig. 4.5). All critical operations and process steps should be
validated, including the cleaning and sanitization of clean rooms and equip-
ment surfaces, the capability of product filters to remove microbiological
contamination, equipment operation, formulation, sterilization of product
contact surfaces, and aseptic practices [16, 17].
Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
Process Process Continuous process
design qualification verification
Based on
product quality know the know the have the
and patient process variables confidence vigilance
safety
1. Process 2. Process 3. Process 4. Commercial 5. Monitoring
and
understanding design qualification manufacture improvement
Change control
CQAs, Parameters, Support system qualification Continuous process verification
Requirements variables, Commissioning Monitoring
control IQ,OQ, PQ Reaction to issues
strategy D.O.E., Statistical sampling Process improvement
plans
Aseptic process simulation
Fig. 4.5 Process validation lifecycle.