Page 19 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 19
Piston-engine cycles of operation CHAPTER 1.1
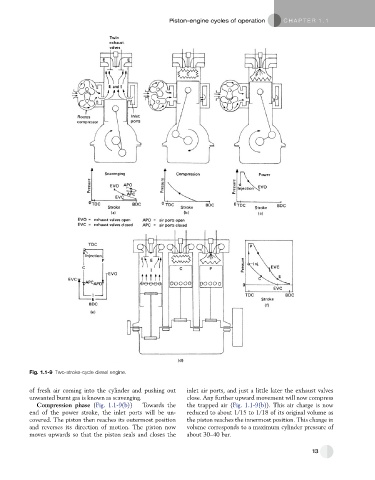
Fig. 1.1-9 Two-stroke-cycle diesel engine.
of fresh air coming into the cylinder and pushing out inlet air ports, and just a little later the exhaust valves
unwanted burnt gas is known as scavenging. close. Any further upward movement will now compress
Compression phase (Fig. 1.1-9(b)) Towards the the trapped air (Fig. 1.1-9(b)). This air charge is now
end of the power stroke, the inlet ports will be un- reduced to about 1/15 to 1/18 of its original volume as
covered. The piston then reaches its outermost position the piston reaches the innermost position. This change in
and reverses its direction of motion. The piston now volume corresponds to a maximum cylinder pressure of
moves upwards so that the piston seals and closes the about 30–40 bar.
13