Page 14 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 14
CH AP TER 1 .1 Piston-engine cycles of operation
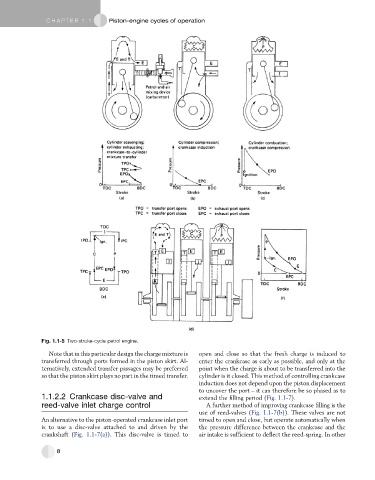
Fig. 1.1-5 Two-stroke-cycle petrol engine.
Note that in this particular design the charge mixture is open and close so that the fresh charge is induced to
transferred through ports formed in the piston skirt. Al- enter the crankcase as early as possible, and only at the
ternatively, extended transfer passages may be preferred point when the charge is about to be transferred into the
so that the piston skirt plays no part in the timed transfer. cylinder is it closed. This method of controlling crankcase
induction does not depend upon the piston displacement
to uncover the port – it can therefore be so phased as to
1.1.2.2 Crankcase disc-valve and extend the filling period (Fig. 1.1-7).
reed-valve inlet charge control A further method of improving crankcase filling is the
use of reed-valves (Fig. 1.1-7(b)). These valves are not
An alternative to the piston-operated crankcase inlet port timed to open and close, but operate automatically when
is to use a disc-valve attached to and driven by the the pressure difference between the crankcase and the
crankshaft (Fig. 1.1-7(a)). This disc-valve is timed to air intake is sufficient to deflect the reed-spring. In other
8