Page 644 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 644
CHAP TER 1 8. 2 Materials for consideration and use in automotive body structures
500 500
ZStE 180/220 BH DP-K 34/60
400 (cold rolled) 400 (cold rolled)
300 300
200
200
Yield strength increase (MPa) 500 0 0 RA-K 42/80 6 8 10 12 14 16 500 0 0 MS-W 4 6 CP-W 8 10 MS-W, CP-W 16
100
100
14
2
4
12
2
(cold rolled)
400
400
(hot rolled)
300
300
200
100
100 200
0 0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Prestrain (%) Work hardening Bake hardening
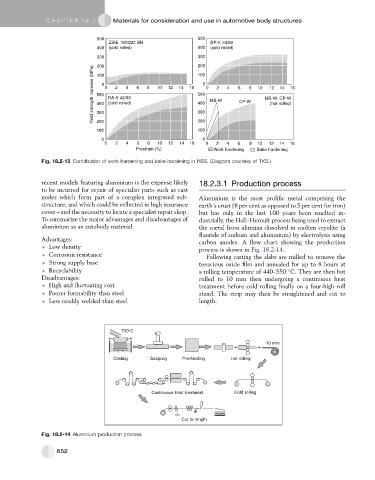
Fig. 18.2-13 Contribution of work hardening and bake hardening in HSS. (Diagram courtesy of TKS.)
recent models featuring aluminium is the expense likely 18.2.3.1 Production process
to be incurred for repair of specialist parts such as cast
nodes which form part of a complex integrated sub- Aluminium is the most prolific metal comprising the
structure, and which could be reflected in high insurance earth’s crust (8 per cent as opposed to 5 per cent for iron)
cover – and the necessity to locate a specialist repair shop. but has only in the last 100 years been smelted in-
To summarize the major advantages and disadvantages of dustrially, the Hall–Heroult process being used to extract
aluminium as an autobody material: the metal from alumina dissolved in molten cryolite (a
fluoride of sodium and aluminium) by electrolysis using
Advantages: carbon anodes. A flow chart showing the production
Low density process is shown in Fig. 18.2-14.
Corrosion resistance Following casting the slabs are milled to remove the
Strong supply base tenacious oxide film and annealed for up to 8 hours at
Recyclability a rolling temperature of 440–550 C. They are then hot
Disadvantages: rolled to 10 mm then undergoing a continuous heat
High and fluctuating cost treatment before cold rolling finally on a four-high roll
Poorer formability than steel stand. The strip may then be straightened and cut to
Less readily welded than steel length.
700°C
10 mm
Casting Scalping Pre-heating Hot rolling
Continuous heat treatment Cold rolling
Cut to length
Fig. 18.2-14 Aluminium production process.
652