Page 69 - Automotive Engineering
P. 69
CH AP TER 3 .1 Emissions control
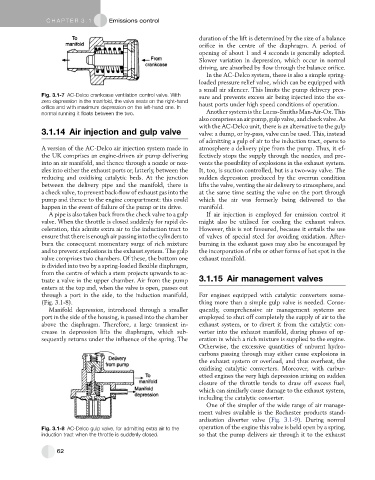
duration of the lift is determined by the size of a balance
orifice in the centre of the diaphragm. A period of
opening of about 1 and 4 seconds is generally adopted.
Slower variation in depression, which occur in normal
driving, are absorbed by flow through the balance orifice.
In the AC-Delco system, there is also a simple spring-
loaded pressure relief valve, which can be equipped with
a small air silencer. This limits the pump delivery pres-
Fig. 3.1-7 AC-Delco crankcase ventilation control valve. With sure and prevents excess air being injected into the ex-
zero depression in the manifold, the valve seats on the right-hand haust ports under high speed conditions of operation.
orifice and with maximum depression on the left-hand one. In
normal running it floats between the two. Another system is the Lucas-Smiths Man-Air-Ox. This
also comprises an air pump, gulp valve, and check valve. As
with the AC-Delco unit, there is an alternative to the gulp
3.1.14 Air injection and gulp valve valve: a dump, or by-pass, valve can be used. This, instead
of admitting a gulp of air to the induction tract, opens to
A version of the AC-Delco air injection system made in atmosphere a delivery pipe from the pump. Thus, it ef-
the UK comprises an engine-driven air pump delivering fectively stops the supply through the nozzles, and pre-
into an air manifold, and thence through a nozzle or noz- vents the possibility of explosions in the exhaust system.
zles into either the exhaust ports or, latterly, between the It, too, is suction controlled, but is a two-way valve. The
reducing and oxidising catalytic beds. At the junction sudden depression produced by the overrun condition
between the delivery pipe and the manifold, there is lifts the valve, venting the air delivery to atmosphere, and
a check valve, to prevent back-flow of exhaust gas into the at the same time seating the valve on the port through
pump and thence to the engine compartment: this could which the air was formerly being delivered to the
happen in the event of failure of the pump or its drive. manifold.
A pipe is also taken back from the check valve to a gulp If air injection is employed for emission control it
valve. When the throttle is closed suddenly for rapid de- might also be utilised for cooling the exhaust valves.
celeration, this admits extra air to the induction tract to However, this is not favoured, because it entails the use
ensure that there is enough air passing into the cylinders to of valves of special steel for avoiding oxidation. After-
burn the consequent momentary surge of rich mixture burning in the exhaust gases may also be encouraged by
and to prevent explosions in the exhaust system. The gulp the incorporation of ribs or other forms of hot spot in the
valve comprises two chambers. Of these, the bottom one exhaust manifold.
is divided into two by a spring-loaded flexible diaphragm,
from the centre of which a stem projects upwards to ac-
tuate a valve in the upper chamber. Air from the pump 3.1.15 Air management valves
enters at the top and, when the valve is open, passes out
through a port in the side, to the induction manifold, For engines equipped with catalytic converters some-
(Fig. 3.1-8). thing more than a simple gulp valve is needed. Conse-
Manifold depression, introduced through a smaller quently, comprehensive air management systems are
port in the side of the housing, is passed into the chamber employed to shut off completely the supply of air to the
above the diaphragm. Therefore, a large transient in- exhaust system, or to divert it from the catalytic con-
crease in depression lifts the diaphragm, which sub- verter into the exhaust manifold, during phases of op-
sequently returns under the influence of the spring. The eration in which a rich mixture is supplied to the engine.
Otherwise, the excessive quantities of unburnt hydro-
carbons passing through may either cause explosions in
the exhaust system or overload, and thus overheat, the
oxidising catalytic converters. Moreover, with carbur-
etted engines the very high depression arising on sudden
closure of the throttle tends to draw off excess fuel,
which can similarly cause damage to the exhaust system,
including the catalytic converter.
One of the simpler of the wide range of air manage-
ment valves available is the Rochester products stand-
ardisation diverter valve (Fig. 3.1-9). During normal
Fig. 3.1-8 AC-Delco gulp valve, for admitting extra air to the operation of the engine this valve is held open by a spring,
induction tract when the throttle is suddenly closed. so that the pump delivers air through it to the exhaust
62