Page 49 - Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 49
32 Autonomous Mobile Robots
L
a homography H (abbreviated from H ladar to image) that maps X to x.
I
3×3
x = HX: H ∈ R (1.17)
This mapping is unambiguous and is parameterized by the geometry
between the two sensors which is less uncertain than the geometry with
reference to a world coordinate system. H can be solved from point
correspondences and if required it can be decomposed into the geometric
parameters relating the two planes.
The reverse mapping is not unambiguous: a point x is the image of the ray
passing through x and the optical center O C . We can map x (with H −1 )toa
single point p {r, θ} in the laser parameter space but there is no guarantee that
the true 3D point that gave rise to x in the image came from this plane. Another
consideration is that image-ladar correspondences are rarely point-to-point but
line-to-point. (ladar data rarely comes from a distinct point in 3D; it is more
likely to have come from a set of points such as a vertical edge or the surface of
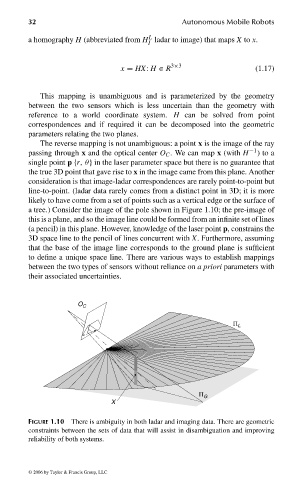
a tree.) Consider the image of the pole shown in Figure 1.10; the pre-image of
this is a plane, and so the image line could be formed from an infinite set of lines
(a pencil) in this plane. However, knowledge of the laser point p, constrains the
3D space line to the pencil of lines concurrent with X. Furthermore, assuming
that the base of the image line corresponds to the ground plane is sufficient
to define a unique space line. There are various ways to establish mappings
between the two types of sensors without reliance on a priori parameters with
their associated uncertainties.
O C
Π L
Π G
X
FIGURE 1.10 There is ambiguity in both ladar and imaging data. There are geometric
constraints between the sets of data that will assist in disambiguation and improving
reliability of both systems.
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
FRANKL: “dk6033_c001” — 2006/3/31 — 16:42 — page 32 — #32