Page 22 - Basic Gas Chromatography
P. 22
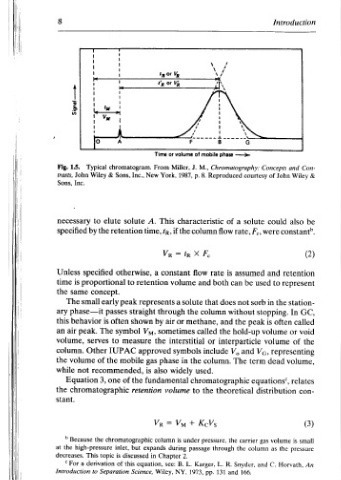
Introduction 9 Disadvantages and Advantages Overview: retention, for stand S and M, R, subscripts the and volume a represents V of volumes the represent Vs and Vy respectively. stationary, and mobile, retention The respectively. column the in phase stationary and phase mobile 1.5. Figure to reference by described be can Vp volume, by deduced be can pro
——> Chromatography: courtesy solute a F., flow rate, assumed used be can sorb not without peak the hold-up interparticle Vg, and V, term The theoretical gas carrier column the Snyder, and 166.
phase Reproduced of is does and the the through R. and
Nu mobile of M., J. 8. p. characteristic column X F, rate flow both and that column methane, called or include column. the used. chromatographic the to KcVs pressure, passage L. Karger, 131 pp. 1973,
Time From York, New This A. tp, time, Ve a retention represents by Vy, the approved phase gas also is fundamental retention = Ve column expands in Chapter equation, Wiley,
thork, or volume Miller, 1987, if the te = constant volume solute a through the or air sometimes interstitial symbols in widely volume + Vu under is during 2. L. B. see: NY,
p-----|~¥__- chromatogram. Inc., Sons, solute retention otherwise, to peak straight passes shown often symbol measure IUPAC mobile recommended, the of chromatographic but inlet, discussed is this of Science,
| & elute early to the one Separation
> proportional concept. is The of 3, topic
Typical Wiley to by the specified serves Other chromatographic the derivation
ae eee small phase—it behavior peak. high-pressure This to
+—— Jeubis 1.5. John Inc. necessary specified Unless is same The air volume, column. volume not Equation Because the decreases. a “For Introduction
Fig. trasts, Sons, time the ary this the while the stant. >
8 an at