Page 370 - Battery Reference Book
P. 370
Float life characteristics 33/19
If float charging is carried out within the recom-
mended limits, the batteries are likely to withstand
overcharge for several years without significant de-
terioration occurring. The number of charge/discharge
cycles obtained from a battery during its life (Le. the
cyclic life) is dependent on the depth of discharge
(i.e. percentage of nominal capacity discharged) to
which it is subjected on discharge. Thus one sup-
plier of lead-acid batteries for standby applications P I I I I I I 1 I
Y
(Crompton-Parkinson) claims a cyclic life of 200 2 0 200 4M) 600 800 1000 1200 1400
cycles when the batteries are on deep discharge duty Number of cycles
(i.e. 80% of nominal capacity still delivered after 200
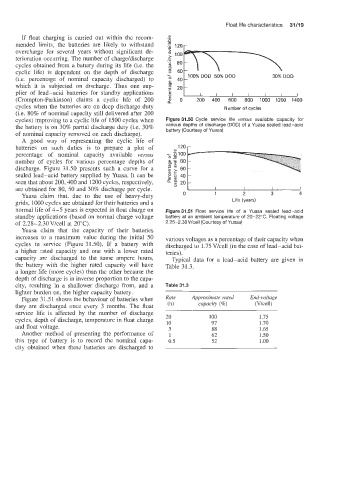
cycles) improving to a cyclic life of 1500 cycles when Figure 31.50 Cycle service life versus available capacity for
the battery is on 30% partial discharge duty (i.e. 30% various depths of discharge (DOD) of a Yuasa sealed lead-acid
battery (Courtesy of Yuasa)
of nominal capacity removed on each discharge).
A good way of representing the cyclic life of
batteries on such duties is to prepare a plot of 120 r
percentage of nominal capacity available versus
number of cycles for various percentage depths of
discharge. Figure 31.50 presents such a curve for a
sealed lead-acid battery supplied by Yuasa. It can be
seen that about 200,400 and 1200 cycles, respectively,
are obtained for 80, 50 and 30% discharge per cycle. I I I J
Yuasa claim that, due to the use of heavy-duty 0 1 2 3 4
grids, 1000 cycles are obiained for their batteries and a Life (years)
norma! life of 4-5 years is expected in float charge on Figure3151 Float service life of a Yuasa sealed lead-acid
standby applications (based on normal charge voltage battery at an ambient temperature of 20-22°C. Floating voltage
of 2.28-2.30Vlcell at 20°C). 2.25-2.30V/cell (Courtesy of Yuasa)
Yuasa claim that the capacity of their batteries
increases to a maximum value during the initial 50 various voltages as a percentage of their capacity when
cycles in service (Figure 31.50). If a battery with discharged to 1.75 V/cell (in the case of lead-acid bat-
a higher rated capacity and one with a lower rated teries).
capacity are discharged to the same ampere hours, Typical data for a lead-acid battery are given in
the battery with the higher rated capacity will have Table 31.3.
a longer life (more cycles) than the other because the
depth of discharge is in inverse proportion to the capa-
city, resulting in a shallower discharge from, and a Table 31.3
lighter burden on, the higher capacity battery.
Figure 3 1.5 i shows the behaviour of batteries when Rate Approximate rated End-voltage
they are discharged once every 3 months. The float (h) capacity ('36) (Vlcell)
service life is affected by the number of discharge 20 100 1.75
cycles, depth of discharge, temperature in float charge 10 97 1.70
and float voltage. 5 88 1.65
Another method of presenting the performance of 1 62 1 SO
this type of battery is to record the nominal capa- 0.5 52 1 .oo
city obtained when these batteries are discharged to