Page 224 - Becoming Metric Wise
P. 224
215
Indicators
likely that they gain new citations, it seems that the m-quotient might
disfavor older scientists. Yet, this has not been tested on a large scale.
7.4.4 Year-Based h-indices
In (Mahbuba & Rousseau, 2013, 2016) three groups of year-based
h-indices were introduced. The first group of year-based h-type indices is
defined as follows. We consider a scientist and all their articles published
over some period of time (this can be their complete career). For each
year we consider the number of publications, the total number of cita-
tions received by these publications during a given period (the citation
window), and the average number of citations per year, leading to three
variations of year-based h-indices. This citation window may be a fixed
period or all years since publication.
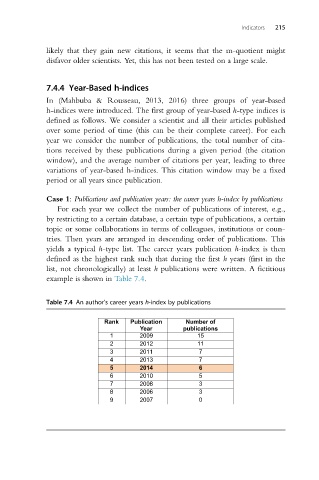
Case 1: Publications and publication years: the career years h-index by publications
For each year we collect the number of publications of interest, e.g.,
by restricting to a certain database, a certain type of publications, a certain
topic or some collaborations in terms of colleagues, institutions or coun-
tries. Then years are arranged in descending order of publications. This
yields a typical h-type list. The career years publication h-index is then
defined as the highest rank such that during the first h years (first in the
list, not chronologically) at least h publications were written. A fictitious
example is shown in Table 7.4.
Table 7.4 An author’s career years h-index by publications
Rank Publication Number of
Year publications
1 2009 15
2 2012 11
3 2011 7
4 2013 7
5 2014 6
6 2010 5
7 2008 3
8 2006 3
9 2007 0