Page 451 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 451
A Damage Model for Estimating Low Cycle Fatigue Lives Under Nonproportional Multiaxial Loading 435
As shown by the equation, by increasing the number of steps in the step loadings, also the
number of terms in the second equation increase, but the damage for each term is decreased,
which results in a smaller value of dll. Therefore, in the step-straining tests with very small
length of steps such as Case 6, da takes values small enough to be ignored, so that the total
damage can be approximated by that of proportional straining tests.
The above showed the equations of nonproportional LCF damage for typical cases of strain
paths in this model. In the next section, by comparing nonproportional LCF lives obtained from
experiments and calculations in which the total damage in Eq.(7) takes unity, i.e., D=l, the
applicability of the presented model for nonproportional LCF life evaluation will be discussed.
CORRELATION OF NONPROPORTIONAL LCF DATA
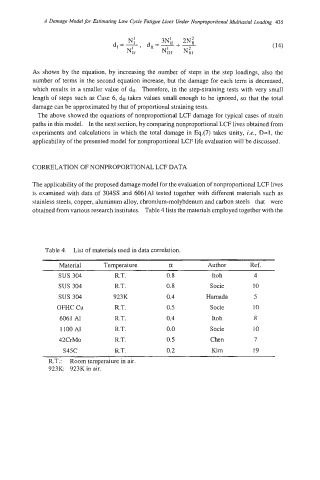
The applicability of the proposed damage model for the evaluation of nonproportional LCF lives
is examined with data of 304SS and 6061A1 tested together with different materials such as
stainless steels, copper, aluminum alloy, chromium-molybdenum and carbon steels that were
obtained from various research institutes. Table 4 lists the materials employed together with the
Table 4. List of materials used in data correlation.
Material Temperature a Author Ref.
sus 304 R.T. 0.8 Itoh 4
SUS 304 R.T. 0.8 Socie 10
SUS 304 923K 0.4 Hamada 5
OFHC cu R.T. 0.5 Socie 10
6061 AI R.T. 0.4 Itoh 8
I100 AI R.T. 0.0 Socie 10
42CrMo R.T. 0.5 Chen 7
s45c R.T. 0.2 Kim 19
R.T.: Room temperature in air.
923K: 923K in air.