Page 77 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 77
70 CHAPTER 4 TRANSFER LEARNING AND SUPERVISED CLASSIFIER
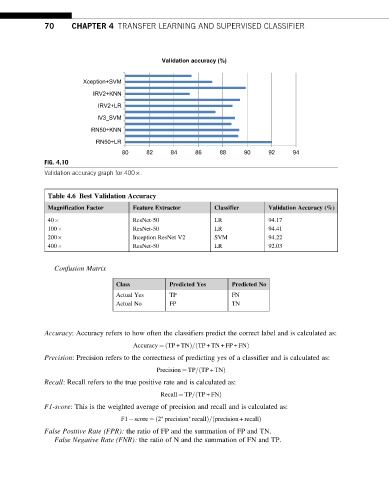
Validation accuracy (%)
Xception+SVM
IRV2+KNN
IRV2+LR
IV3_SVM
RN50+KNN
RN50+LR
80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94
FIG. 4.10
Validation accuracy graph for 400 .
Table 4.6 Best Validation Accuracy
Magnification Factor Feature Extractor Classifier Validation Accuracy (%)
40 ResNet-50 LR 94.17
100 ResNet-50 LR 94.41
200 Inception ResNet V2 SVM 94.22
400 ResNet-50 LR 92.03
Confusion Matrix
Class Predicted Yes Predicted No
Actual Yes TP FN
Actual No FP TN
Accuracy: Accuracy refers to how often the classifiers predict the correct label and is calculated as:
ð
Accuracy ¼ TP + TNÞ= TP + TN + FP + FNÞ
ð
Precision: Precision refers to the correctness of predicting yes of a classifier and is calculated as:
Precision ¼ TP= TP + TNÞ
ð
Recall: Recall refers to the true positive rate and is calculated as:
ð
Recall ¼ TP= TP + FNÞ
F1-score: This is the weighted average of precision and recall and is calculated as:
F1 score ¼ 2 ∗ precision ∗ recallÞ= precision + recallÞ
ð
ð
False Positive Rate (FPR): the ratio of FP and the summation of FP and TN.
False Negative Rate (FNR): the ratio of N and the summation of FN and TP.