Page 51 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 51
3.2 Monoclonal antibody-based immune assays 49
used for quantitation of CA215 in serum specimens of patients with cancer. RP215
has been used as the unique probe for cancer diagnosis.
A comparative research list of the positive rates of serum CA215 levels in dif-
ferent types of cancer including: lung (52%), colon (44%), ovary (59%), breast
(38%), pancreas (51%) esophagus (61%), stomach (60%), kidney (38%), and lym-
phoma (83%) [11]. Immunohistochemically tissue staining studies with RP215 as
the immune probe for cancerous antigen receptors also have indicated widespread
expressions of RP215-epitope among various cancer tissues. Among these, the
results were: ovary (n = 87, 64.4%), cervix (n = 51, 84.3%), endometrium (n = 36,
77.8%), stomach (n = 93, 49.5%), colon (n = 87, 43.6%), esophagus (n = 56, 75.7%),
lung (n = 58, 31%), and breast (n = 59, 32.2%). In contrast, low percentages of posi-
tive tissue staining were observed for the cancer of liver (n = 60, 3.5%) and prostate
(n = 22, 10%). Based on the results, RP215 could be a unique probe for cancer diag-
nosis [12,13].
In recent years, evidence of circulating autoantibodies in the sera of patients with
cancer have created opportunities for utilizing the immune system as a source of
cancer biomarkers. Autoantibodies are used as serum biomarkers which show highly
appealing features. The persistence and stability of autoantibodies in the serum of
patients is a good point over other potential markers that have been currently utilized.
Autoantibodies are available in the sera before of TAAs can be detected (if they are).
They correspond to an effective biological amplification of the presence of TAAs,
and are released in the serum prior to initial clinical symptoms. Moreover, antibod-
ies are highly stable in serum samples and are not subjected to proteolysis like other
polypeptides, making sample handling much easier. They have shown a long life-
time (half-life between 7 and 30 days, depending on the type of Ig) in the blood
and may persist as long as the corresponding autoantigen creates a specific humoral
response. A few researches have attempted to identify panels of autoantibodies for
early diagnosis of breast cancer. The results were favorable, in some patients sensi-
tivities above 70% [14,15].
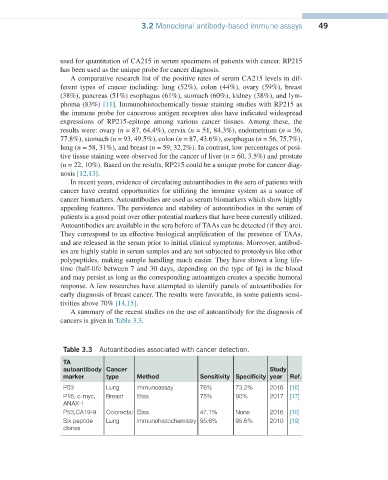
A summary of the recent studies on the use of autoantibody for the diagnosis of
cancers is given in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3 Autoantibodies associated with cancer detection.
TA
autoantibody Cancer Study
marker type Method Sensitivity Specificity year Ref.
P53 Lung Immunoassay 76% 73.2% 2016 [16]
P16, c-myc, Breast Elisa 75% 90% 2017 [17]
ANAX-1
P53,CA19-9 Colorectal Elisa 47.1% None 2016 [18]
Six peptide Lung Immunohistochemistry 95.6% 95.6% 2010 [19]
clones