Page 49 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 49
3.2 Monoclonal antibody-based immune assays 47
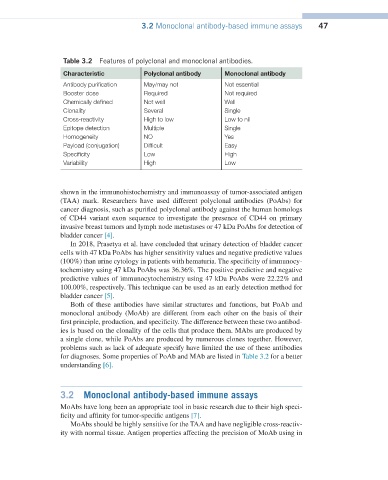
Table 3.2 Features of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies.
Characteristic Polyclonal antibody Monoclonal antibody
Antibody purification May/may not Not essential
Booster dose Required Not required
Chemically defined Not well Well
Clonality Several Single
Cross-reactivity High to low Low to nil
Epitope detection Multiple Single
Homogeneity NO Yes
Payload (conjugation) Difficult Easy
Specificity Low High
Variability High Low
shown in the immunohistochemistry and immunoassay of tumor-associated antigen
(TAA) mark. Researchers have used different polyclonal antibodies (PoAbs) for
cancer diagnosis, such as purified polyclonal antibody against the human homologs
of CD44 variant exon sequence to investigate the presence of CD44 on primary
invasive breast tumors and lymph node metastases or 47 kDa PoAbs for detection of
bladder cancer [4].
In 2018, Prasetya et al. have concluded that urinary detection of bladder cancer
cells with 47 kDa PoAbs has higher sensitivity values and negative predictive values
(100%) than urine cytology in patients with hematuria. The specificity of immunocy-
tochemistry using 47 kDa PoAbs was 36.36%. The positive predictive and negative
predictive values of immunocytochemistry using 47 kDa PoAbs were 22.22% and
100.00%, respectively. This technique can be used as an early detection method for
bladder cancer [5].
Both of these antibodies have similar structures and functions, but PoAb and
monoclonal antibody (MoAb) are different from each other on the basis of their
first principle, production, and specificity. The difference between these two antibod-
ies is based on the clonality of the cells that produce them. MAbs are produced by
a single clone, while PoAbs are produced by numerous clones together. However,
problems such as lack of adequate specify have limited the use of these antibodies
for diagnoses. Some properties of PoAb and MAb are listed in Table 3.2 for a better
understanding [6].
3.2 Monoclonal antibody-based immune assays
MoAbs have long been an appropriate tool in basic research due to their high speci-
ficity and affinity for tumor-specific antigens [7].
MoAbs should be highly sensitive for the TAA and have negligible cross-reactiv-
ity with normal tissue. Antigen properties affecting the precision of MoAb using in