Page 84 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 84
82 CHAPTER 4 Immunotherapy
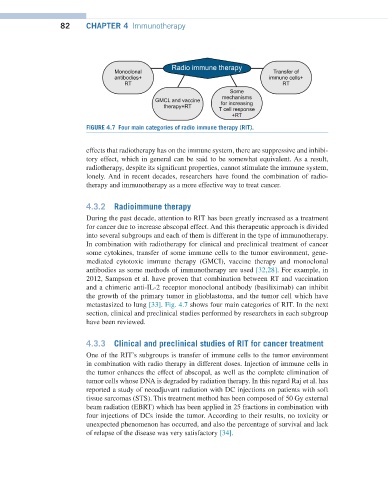
FIGURE 4.7 Four main categories of radio immune therapy (RIT).
effects that radiotherapy has on the immune system, there are suppressive and inhibi-
tory effect, which in general can be said to be somewhat equivalent. As a result,
radiotherapy, despite its significant properties, cannot stimulate the immune system,
lonely. And in recent decades, researchers have found the combination of radio-
therapy and immunotherapy as a more effective way to treat cancer.
4.3.2 Radioimmune therapy
During the past decade, attention to RIT has been greatly increased as a treatment
for cancer due to increase abscopal effect. And this therapeutic approach is divided
into several subgroups and each of them is different in the type of immunotherapy.
In combination with radiotherapy for clinical and preclinical treatment of cancer
some cytokines, transfer of some immune cells to the tumor environment, gene-
mediated cytotoxic immune therapy (GMCI), vaccine therapy and monoclonal
antibodies as some methods of immunotherapy are used [32,28]. For example, in
2012, Sampson et al. have proven that combination between RT and vaccination
and a chimeric anti-IL-2 receptor monoclonal antibody (basiliximab) can inhibit
the growth of the primary tumor in glioblastoma, and the tumor cell which have
metastasized to lung [33]. Fig. 4.7 shows four main categories of RIT. In the next
section, clinical and preclinical studies performed by researchers in each subgroup
have been reviewed.
4.3.3 Clinical and preclinical studies of RIT for cancer treatment
One of the RIT’s subgroups is transfer of immune cells to the tumor environment
in combination with radio therapy in different doses. Injection of immune cells in
the tumor enhances the effect of abscopal, as well as the complete elimination of
tumor cells whose DNA is degraded by radiation therapy. In this regard Raj et al. has
reported a study of neoadjuvant radiation with DC injections on patients with soft
tissue sarcomas (STS). This treatment method has been composed of 50 Gy external
beam radiation (EBRT) which has been applied in 25 fractions in combination with
four injections of DCs inside the tumor. According to their results, no toxicity or
unexpected phenomenon has occurred, and also the percentage of survival and lack
of relapse of the disease was very satisfactory [34].