Page 82 - Bio Engineering Approaches to Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
P. 82
80 CHAPTER 4 Immunotherapy
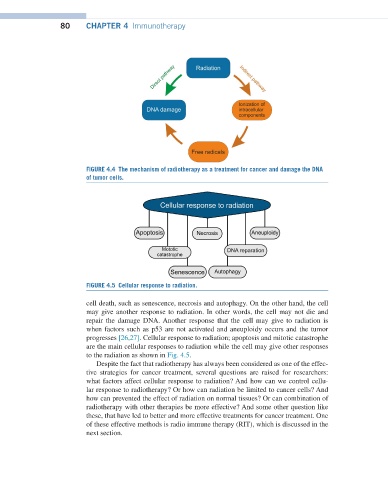
FIGURE 4.4 The mechanism of radiotherapy as a treatment for cancer and damage the DNA
of tumor cells.
FIGURE 4.5 Cellular response to radiation.
cell death, such as senescence, necrosis and autophagy. On the other hand, the cell
may give another response to radiation. In other words, the cell may not die and
repair the damage DNA. Another response that the cell may give to radiation is
when factors such as p53 are not activated and aneuploidy occurs and the tumor
progresses [26,27]. Cellular response to radiation; apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe
are the main cellular responses to radiation while the cell may give other responses
to the radiation as shown in Fig. 4.5.
Despite the fact that radiotherapy has always been considered as one of the effec-
tive strategies for cancer treatment, several questions are raised for researchers:
what factors affect cellular response to radiation? And how can we control cellu-
lar response to radiotherapy? Or how can radiation be limited to cancer cells? And
how can prevented the effect of radiation on normal tissues? Or can combination of
radiotherapy with other therapies be more effective? And some other question like
these, that have led to better and more effective treatments for cancer treatment. One
of these effective methods is radio immune therapy (RIT), which is discussed in the
next section.